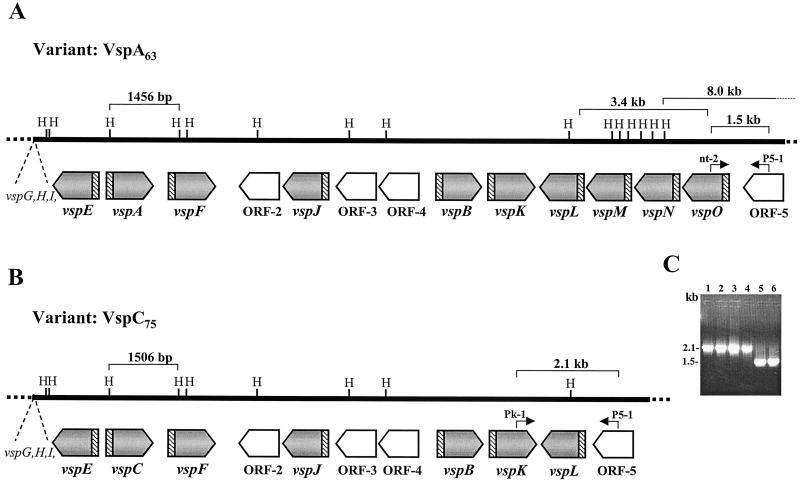
FIG. 3.
Comparison of the M. bovis vsp genomic loci from the VspA clonal isolate expressing a 63-kDa VspA protein (A) and from a VspC clonal isolate expressing a 75-kDa product (B). The locations and orientations of the vsp genes in each locus are shown by shaded and labeled arrows. Four non-vsp ORFs (ORF-2 to ORF-5) are shown by open labeled arrows. Positions of HindIII (H) restriction sites are marked. The highly conserved vsp-upstream region is shown by hatched blocks. Locations of a 1,456-bp HindIII fragment carrying the vspA gene in the VspA isolate, of a 1,506-bp HindIII fragment carrying the vspC gene in the VspC isolate, and of a 3.4-kb fragment carrying vspM, vspN, and part of the vspO gene of the VspA isolate that is missing in the VspC isolate are indicated by brackets. The 5′ end of an 8.0-kb HindIII genomic fragment (Fig. 5A, lane 1) in the VspA isolate is marked. Locations of two sets of PCR primers (P5-1/nt-2 and P5-1/Pk-1) as well as sizes of the resultant PCR products (1.5 and 2.1 kb, respectively) are marked. (C) PCR amplification of M. bovis isolates. PCR primers P5-1 and Pk-1 were used to amplify the corresponding genomic regions of isolates 168 (VspC75) (lane 1), 166 (VspC79) (lane 2), and 182 (VspC75) (lane 3) and of M. bovis type strain PG45 (lane 4). PCR primers P5-1 and nt-2 were used to amplify the corresponding genomic region of isolates 7 (VspA63) (lane 5) and M. bovis PG45 (lane 6). Sizes of the PCR products are indicated.