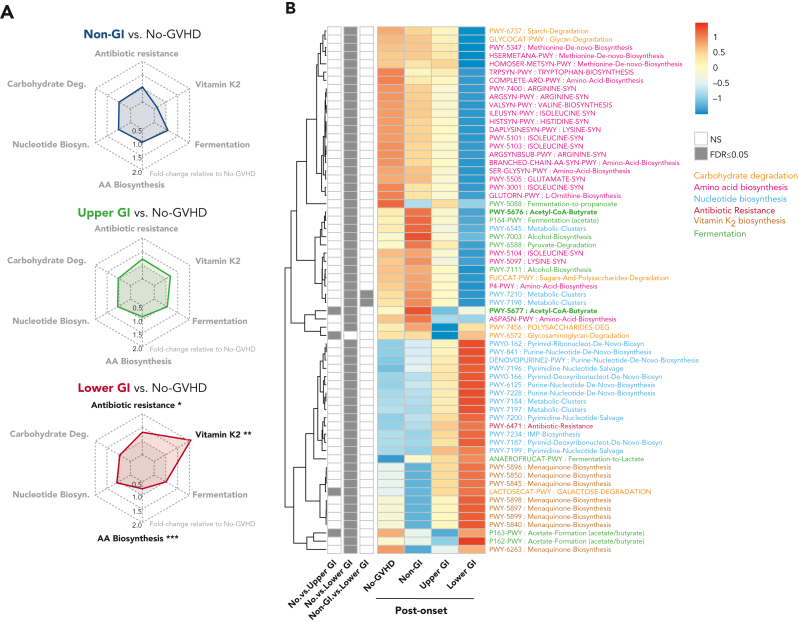
Figure 5.
GVHD patients present distinct postonset predicted PICRUSt pathways. (A) Radar chart representation of PICRUSt predicted functional pathways belonging to 6 main metabolic pathways: carbohydrate degradation, nucleotide biosynthesis, amino acid biosynthesis, antibiotic resistance, vitamin K2 biosynthesis, and fermentation for GVHD patients post-GVHD onset relative to no-GVHD controls. Axis represents fold change relative to no-GVHD patients. (B) Heat map with hierarchical clustering of statistically significant (FDR P ≤ .05) unique PICRUSt pathways. Figure displays pathways found in a minimum of 5% of samples within all groups. LGI GVHD patients show increased abundance of pathways associated with general antibiotic resistance and vitamin K2 metabolism with lower abundance of pathways linked to amino acid biosynthesis relative to no-GVHD patients. Lower abundance of pathways specific to butyrate production was also found in LGI patients compared with no-GVHD controls (bold). ∗FDR P ≤ .05; ∗∗FDR P ≤ .01; ∗∗∗FDR P ≤ .001. NS, not significant.