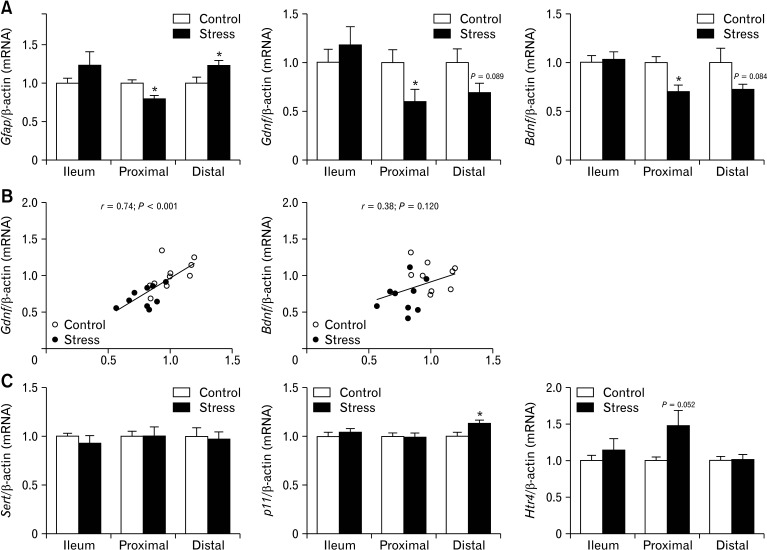
Figure 4.
Chronic stress down-regulate transcripts encoding enteric glia, neurotrophins in proximal colon. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to analyze glial fibrillary acidic protein (Gfap), glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (Gdnf), and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Bdnf) expression levels in small intestine and colon of control and stressed mice (n = 10/group). (A) Transcripts encoding Gfap, Gdnf, and Bdnf were significantly decreased in proximal colon after chronic stress when compared with control mice. (B) In proximal colon also a strong correlation between Gfap and Gdnf expression levels was observed. (C) Expression levels of serotonin transporter, solute carrier family 6 Slc6a4 (Sert), was not different between stressed and control mice, expression levels of S100 calcium binding protein A10 (p11) were significantly increased in distal colon of stress mice and the increase of serotonin receptor 4 (Htr4) receptor mRNA levels were nearly significant in proximal colon of stress mice. Data represent mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05 by t test.