Figure 2.
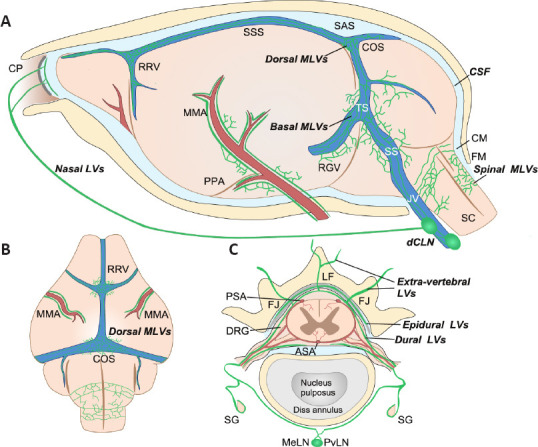
Schematic illustration of the anatomical position of meningeal lymphatic vessels around the mouse brain and spinal cord.
(A) On the lateral side of the mouse brain, MLVs run along the artery (red) and venous sinus (blue). Basal MLVs running along the TS and SS have been identified as the main route for CSF uptake and drainage. Parasinusoidal MLVs develop from LVs along the PPA, the JV, and cranial nerves. Spinal MLVs covering the FM connect to MLVs in the cervical spinal canal. (B) On the dorsal side of the mouse brain, dorsal MLVs run along the RRV, COS, and MMA. (C) Spinal MLVs (or vertebral LVs) are present in the epidural space around the spinal cord and the dura mater. On the dorsal side of the spinal canal, they connect at the midline and extend to the CM. However, they do not form a circuit on the ventral side. Spinal LVs further connect with extra-vertebral peripheral LVs at the ventral border of the LF or the level of the transverse FJ. They cover the dura mater of DRG and contact SG. Longitudinal connecting LVs between vertebral units also exist (not shown). Created with Vectornator. ASA: Anterior spinal artery; CM: cisterna magna; COS: the confluence of the sinuses; CP: cribriform plate; dCLNs: deep cervical lymph nodes; DRG: dorsal root ganglia; FJ: facet joint; FM: foramen magnum; JV: jugular vein; LF: ligamentum flavum; MeLN: mediastinal lymph node; MMA: middle meningeal artery; PPA: pterygopalatine artery; PSA: posterior spinal artery; PvLN: posterior vertebral lymph node; RGV: retroglenoid vein; RRV: rostral rhinal vein; SC: spinal cord; SG: sympathetic ganglia; SS: sigmoid sinus; SSS: superior sagittal sinus; TS: transverse sinus.
