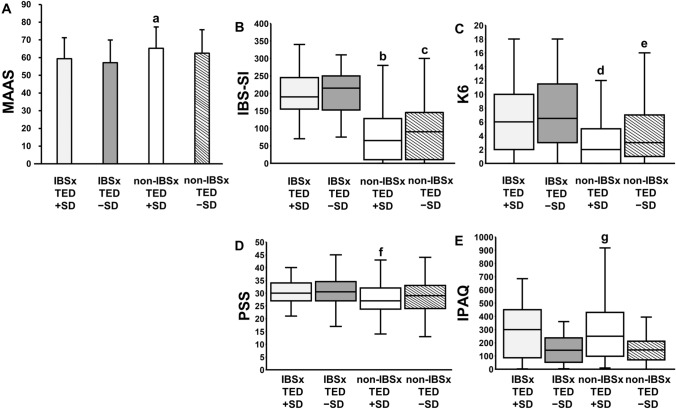
Fig. 1.
Multiple comparisons among groups of IBS × exercise. Mindful Attention Awareness Scale among four groups of IBS × exercise: IBS with more exercise ≧ SD (IBS × TED + SD), IBS with less exercise < SD (IBS × TED − SD), non-IBS with more exercise ≧ SD (non-IBS × TED + SD), and non-IBS with less exercise < SD (non-IBS × TED − SD). A One-way ANOVA: p = 0.004, post hoc (Sidak) test: a vs. IBS × TED − SD, p = 0.005, height: mean, error bar: standard deviation. IBS severity, depression/anxiety, stress, and physical activity among four groups of IBS x exercise. B IBS-SI: Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.001, post hoc (Dunn-Bonferroni multiple comparison) test: b vs. IBS × TED + SD, p < 0.001, and IBS × TED − SD, p < 0.001, c vs. IBS × TED + SD, p < 0.001, and IBS × TED − SD, p < 0.001, C K6: p < 0.001, post hoc: d vs. IBS × TED + SD, p = 0.002, and IBS × TED − SD, p = 0.044, e vs. IBS × TED + SD, p < 0.001, and IBS × TED − SD, p = 0.004, D PSS: p = 0.025, post hoc: f vs. IBS × TED − SD, p = 0.047, E IPAQ: p = 0.002, post hoc: g vs. IBS × TED − SD, p = 0.034, and non-IBS × TED − SD, p = 0.013. height: median, error bar: inter quartile range