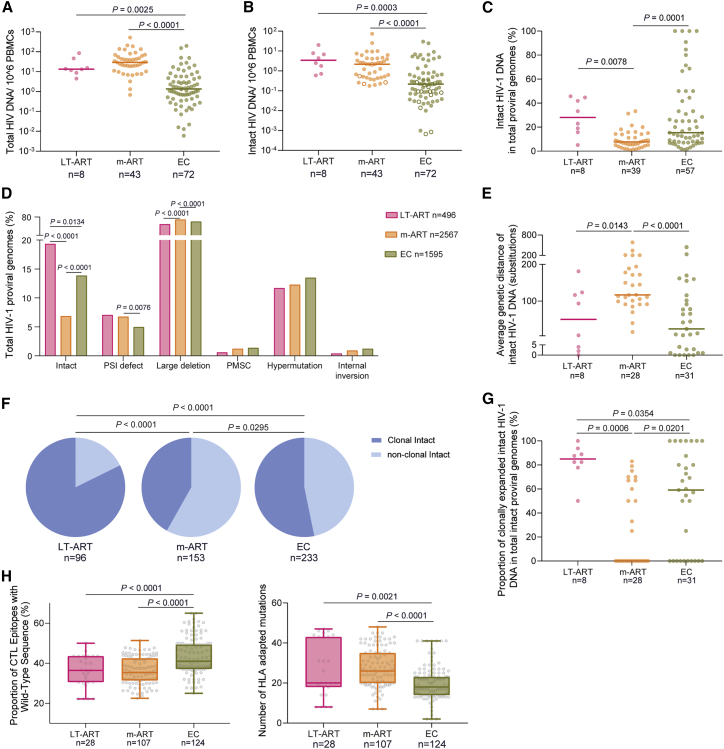
Figure 1.
Proviral reservoir profile in long-term ART-treated individuals
(A and B) Frequency of total (A) and intact (B) HIV-1 proviruses in long-term ART-treated individuals (LT-ART), in people living with HIV (PLHIV) undergoing moderate durations of treatment (median of 9 years) (m-ART), and in elite controllers (ECs). Open circles indicate data at the limit of detection.
(C) Proportion of intact proviruses within total HIV-1 proviruses in indicated study cohorts.
(D) Proportion of proviruses with genome-intact or defective sequences in indicated study cohorts.
(E) Average genetic distance between intact proviruses from indicated study cohorts, determined by pairwise comparisons between all intact proviruses from a given study participant.
(F) Pie charts reflecting proportions of intact proviruses detected once (non-clonal) or multiple times (clonal) in the three indicated study cohorts.
(G) Proportions of clonally expanded intact HIV-1 proviruses within the total pool of intact HIV-1-proviruses from each study participant.
(H) (Left panel) Proportion of wild-type clade B CTL epitopes restricted by autologous HLA class I alleles within intact proviruses from indicated study cohorts. Each symbol represents one intact proviral sequence; all intact clade B sequences were included. (Right panel) Numbers of base pair variations significantly associated with autologous HLA class I alleles, determined as described by Carlson et al.,13 within intact HIV-1 proviruses from indicated study participants. Each symbol reflects one intact provirus. Clonal sequences were counted once. Box and Whisker plots demonstrate median, interquartile ranges, and minimum/maximum.
(A–H) FDR-adjusted two-sided Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric test or FDR-adjusted Fisher’s exact test were used, as appropriate. (A–C, E, and G) Horizontal bars indicate the median and n represents the number of study subjects. (D, F, and H) n reflects the number of viral sequences.