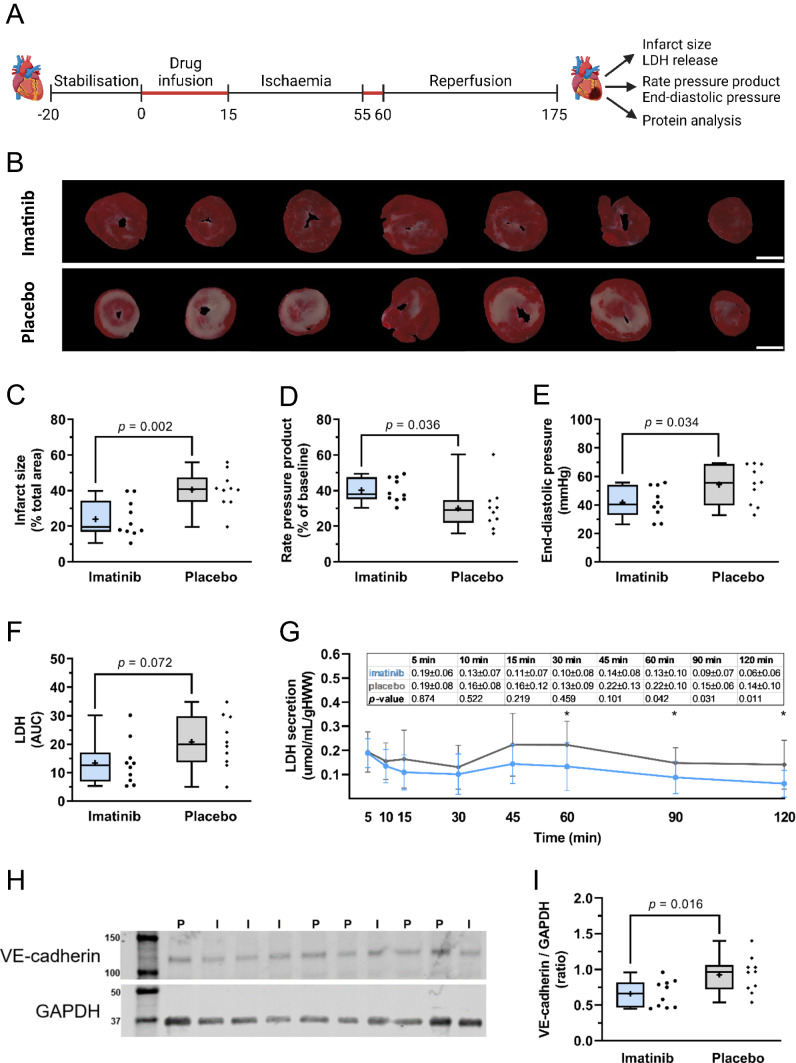
Fig. 1.
Imatinib reduces IR injury in isolated rat hearts. Isolated rat hearts were subjected to 40 min global ischaemia and 120 min reperfusion and assessed for the extent of reperfusion injury. A Hearts were perfused with imatinib or placebo during the first 15 min and the first 5 min of reperfusion (in red). B Representative images of infarct size determined with TTC staining. White scale bar represents 5 mm. C Imatinib reduced global infarct size, D improved rate pressure product recovery, and E decreased end-diastolic pressure at the end of reperfusion. F There was a trend towards reduced total LDH release in the imatinib group. G LDH release (umol/mL/gHWW) during reperfusion. H Representative Western Blots from heart apex. VE-cadherin is detected at ~ 120 kD, GAPDH at ~ 37 kD. I = imatinib, P = placebo. I, Relative densitometric graph after normalisation to GAPDH. Every ● represents one rat (C, D, E, F; blue, imatinib n = 10; grey, placebo; n = 10). The plus sign represents the mean. Data is presented as median with IQR, whiskers min to max (C, D, E, F, I) or mean ± SD (G), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and assessed by independent-samples T test (C, D, E, F, I) or mixed models repeated measures (G). AUC area under the curve during reperfusion, gHWW gram heart wet weight