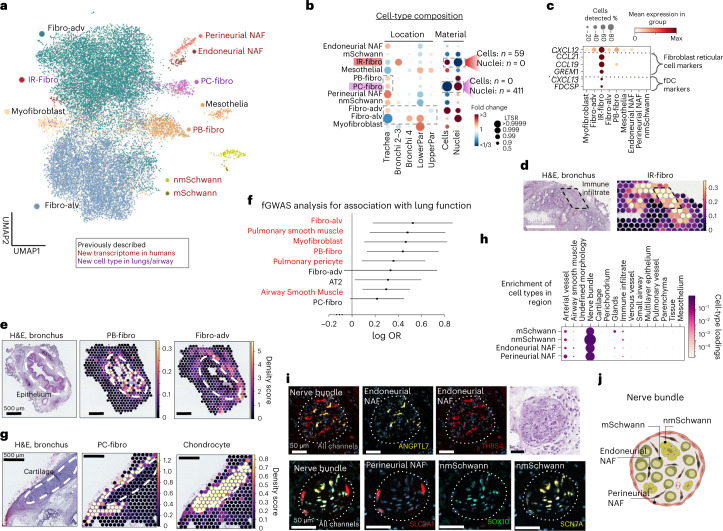
Fig. 2. Lung and airway fibroblasts and their spatial location.
a, Sequential clustering reveals 11 fibroblast populations in airways and lungs on UMAP, colored by novelty as shown. b, Sample collection location and processing method affect cell type proportions. Poisson linear mixed model analysis of cell type composition within the fibroblast compartment, accounting for location, material, dissociation protocol and donor in the model. Cell type numbers are shown in Supplementary Table 7 and in online portal. c, Dot plot of IR-fibro marker genes that overlap with Fibroblast reticular cell and fDC markers. d,e, Cell2location density scores demonstrate that (d) IR-fibro colocalizes with a manually annotated immune infiltrate microenvironment in the airways, and (e) PB-fibro localizes around the airway epithelium. f, PB-fibro are associated with lung function (FEV1/FVC) in fGWAS analysis (logOR, 0.53; FDR, 0.014). Shown are the log odds ratios (logOR) obtained from fGWAS and their Wald confidence intervals (n = 19,414 genes) for several cell types. Substantially enriched cell types are marked in red (Wald test, BH multiple testing correction over 76 cell types, FDR < 0.1). g, Visium ST mapping of PC-fibro around the airway cartilage showing cell2location density scores. h, Schwann cells and NAF colocalize with peripheral nerve bundles in annotated Visium ST sections by cell2location. Cell type loadings are represented by both dot size and color. i, Nerve-associated cell type markers have distinct locations in the airway nerve bundles identified by smFISH staining. Donors used for replicas are shown in Supplementary Table 9. The marker gene probes for each cell type are given in each panel. Dashed lines surround the nerve bundles. j, Schematic representation of the described nerve-associated populations in the peripheral nerves of the airway. Fibro-alv, alveolar fibroblasts; fibro-adv, adventitial fibroblasts.