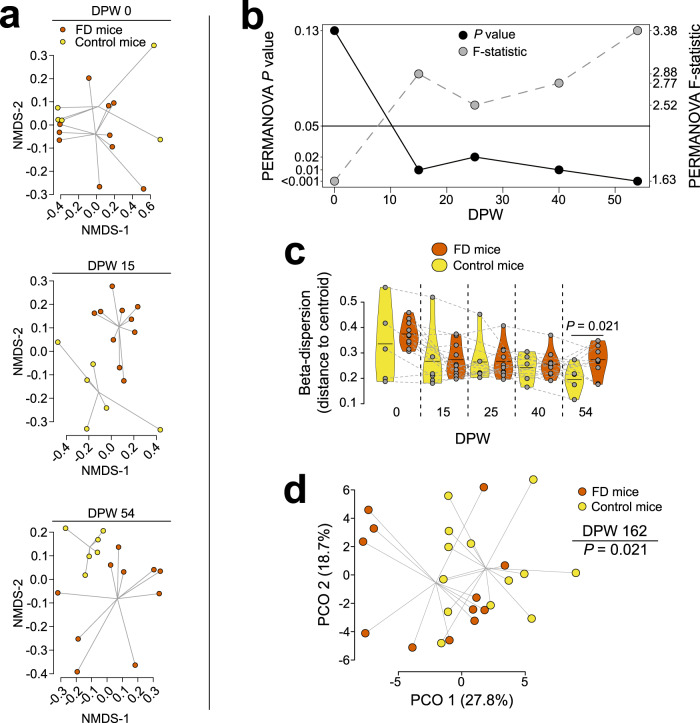
Fig. 3. Neuron-specific Elp1 deletion drives progressive microbiome and metabolome divergence in mice.
a Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of 16 S rRNA-based stool microbiome diversity of FD (Tuba1a-cre+; Elp1loxp/loxp) and control (Tuba1a-cre−; Elp1+/loxp) mice when housed separately by genotype (group colors same for all panels; DPW = days postweaning). b Progressive groupwise differences in microbiome beta-diversity (Bray-Curtis dissimilarity) and (c) dispersion of beta-diversity (beta-dispersion) in FD mice (dotted lines connect individual mice, solid line in violin plots = mean). d Principal coordinates analysis of stool metabolome in mice at 162 DPW. n = a, b, c 10 FD mice (4 female, 6 male; 3 cages), 6 control mice (4 female, 2 male; 2 cages); d, 12 FD mice, 13 control mice (all female; 3 cages per genotype); PERMANOVA (a, b, day 0, df = 1, R2 = 0.1099; day 15, df = 1, R2 = 0.1664; day 25, df = 1, R2 = 0.1458; day 40, df = 1, R2 = 0.1836; day 54, df = 1, R2 = 0.1927; d, F = 2.2086, df = 1, R2 = 0.0876); Welch’s two-sample t-test (c, t-statistic = −2.6589, df = 12.05, difference between FD and control mice = −0.0777, 95% confidence interval of difference between FD and control mice = −0.1414 to −0.0141).