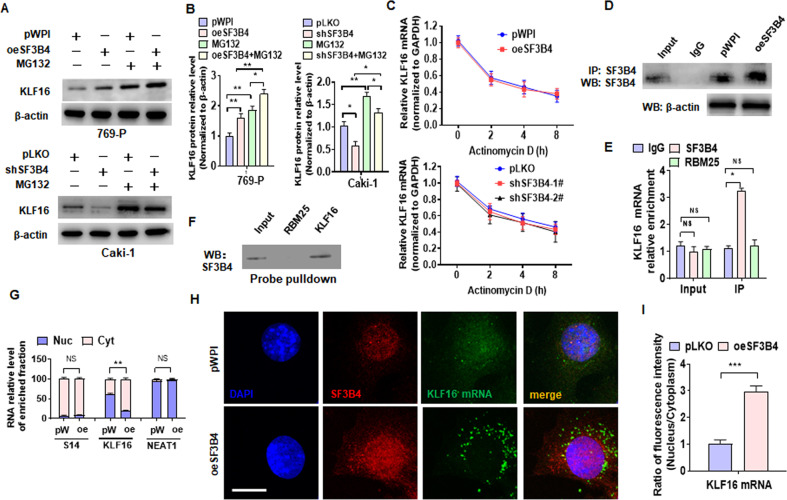
Fig. 6. SF3B4 upregulates KLF16 expression by promoting its mRNA export from the nucleus.
A, B Western blot analysis examined KLF16 expression in MG132-treated cells after oeSF3B4 or shSF3B4 transfection. C The KLF16 mRNA was examined by RT-qPCR in actinomycin D-treated cells after transfection with the indicated constructs. D Caki-1 cells were transfected with oeSF3B4 or empty vector, and SF3B4 in the anti-SF3B4 immunoprecipitates was measured by Western blotting. E RNA binding protein immunoprecipitation assay (RIP) detected KLF16 mRNA enrichment by SF3B4 or RBM25 antibody. F Biotinylated RNA probes of KLF16 mRNA were used to pull down the RNA-protein complex, and the Western blot analysis detected SF3B4 enrichment. G Caki-1 cells were transfected with oeSF3B4 (oe) or pWPI (pW) and then RNA was isolated from the nucleus (Nuc) and cytoplasm (Cyt), mRNA of S14, KLF16, and NEAT RNA was detected by RT-qPCR. S14 acts as plasma-specific RNA and NEAT1 RNA as nucleus-specific RNA. H Caki-1 cells were treated as in G, and the expression of SF3B4 protein and KLF16 mRNA as well as their distribution in the nucleus and cytoplasm were detected by immunofluorescence combined with FISH. SF3B4 antibody (red) was used to detect SF3B4 protein, while the FITC-probe (green) was used to detect KLF16 mRNA. I Quantitative analysis of the KLF16 mRNA distribution in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Scale bar = 5 μm. All data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. their corresponding controls.