Figure 2.
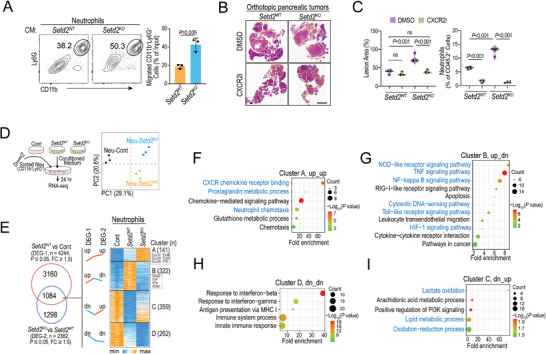
Setd2 loss in pancreatic tumor promotes the recruitment and immunosuppressive phenotype of neutrophils. A) Neutrophil chemotaxis assay using 20% conditioned medium from Setd2 WT or Setd2 KO pancreatic tumor cells. Representative flow cytometry plots and statistical analysis are shown (n = 3). B,C) Orthotopic Setd2 WT and Setd2 KO tumor‐bearing mice were administered CXCR2 antagonist (CXCR2i, SB225002, 1 mg kg−1 every other day) and DMSO as a control for 12 days. B) Pancreatic tissues were collected for H&E staining. C) Quantification of lesion area and percentage of infiltrating neutrophils from the indicated mice (n = 4 per group). Scale bar = 2 mm. D) Neutrophils sorted from bone marrow (BM) were treated with conditioned medium from Setd2 WT or Setd2 KO cells, as well as control medium for 24 h. The above‐primed neutrophils were collected for RNA‐seq. Principal component analysis (PCA) scores plot indicating discrimination among Neu‐Cont, Neu‐Setd2 WT, and Neu‐Setd2 KO (n = 3 per groups). E) Heatmap of RNA‐Seq data to compare the gene expression among the Neu‐Cont, Neu‐Setd2 WT, and Neu‐Setd2 KO groups. F–I) Pathway enrichment of the indicated gene cluster based on RNA‐Seq data. The experiments had three replicates and were repeated three times (A). Data are represented as the mean ± SD (A) or mean ± SEM (C). Statistical differences were determined with unpaired Student's t test in (A), and one‐way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparisons test in (C).
