FIGURE 5.
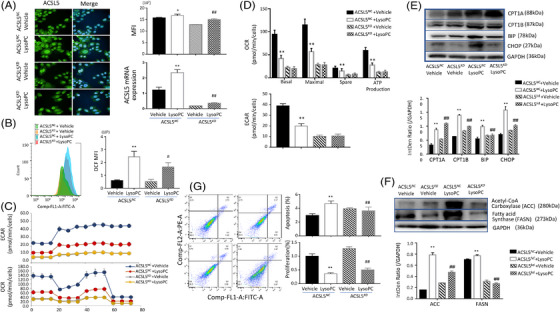
Lysophosphatidylcholine (lysoPC)‐induced mitochondrial dysfunctions through long‐chain acyl‐coenzyme A synthases 5 (ACSL5). LysoPC‐induced alterations of ACSL5 mRNA and protein expression were confirmed in ACSL5 NC and ACSL5 KD cells treated with vehicle or lysoPC for 6 h (A; representative fluorescence image with scale bar at 50 μm, n = 4 per group). Levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (B), oxygen consumption rate (OCR) (C) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) (D) were measured to show critical roles ACSL5 in lysoPC‐changed mitochondrial function (n = 3 per group thrice). Protein levels of CPT1A, CPT1B, BIP and CHOP (F) as well as ACC and FASN (E) were assessed to detect lysoPC‐induced fatty acid hyper‐oxidations and ER dysfunction. Cell apoptosis and proliferation were evaluated (G) to evidence the central role of ACSL5 in inhibitory effects of lysoPC on lung cancer cells). * and ** or # and ## stand for the p‐values less than .05 and .01, respectively, as compared with of ACSL5 NC cells treated with vehicle or lysoPC. CPT1: carnitine palmitoyl transferase I; BIP: binding‐immunoglobulin protein; CHOP: C/EBP‐homologous protein; and GAPDH: glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase
