Figure 7.
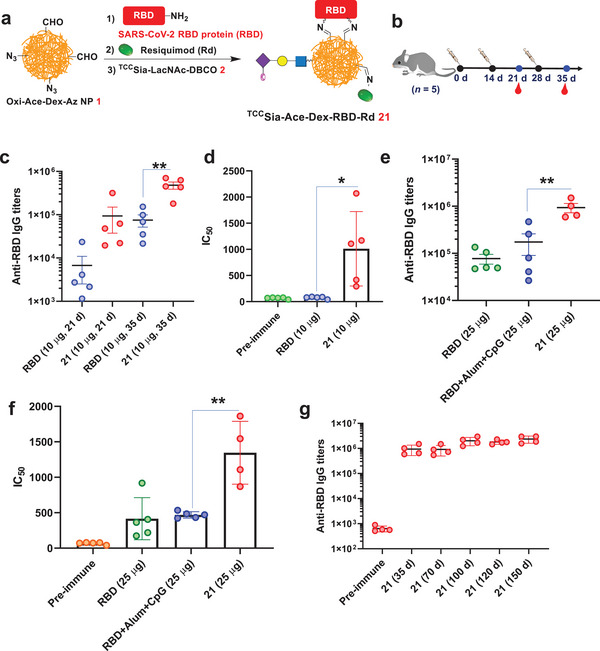
a) Synthesis of TCCSia‐Ace‐Dex‐RBD‐Rd (21). b) Immunization of mice with free receptor‐binding domain (RBD) (10 µg) and 21 (with 10 µg RBD in the nanoparticles, NPs), respectively. c) Titers of anti‐RBD IgG from mice immunized with free RBD and 21, respectively. d) IC50 values of RBD binding to hACE2 by antibodies elicited by free RBD and 21 showed 21‐induced antibodies significantly blocked the SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD binding to hACE2. e–g) Immunization of mice with free RBD (25 µg), 21 (with 25 µg RBD in the NPs), or RBD+Alum+CpG (with 25 µg RBD). e) Titers of anti‐RBD IgG antibodies from mice immunized with free RBD, 21, or RBD+Alum+CpG. f) IC50 determination of RBD binding to hACE2 by IgG elicited by free RBD, RBD+Alum+CpG and 21 showed 21 induced IgG effectively blocked SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD binding to hACE2. g) Persistence of antibody responses induced by 21. Each symbol represents one mouse (n = 4−5 mice for each group). A two‐tailed unpaired Student's t‐test determined the p values with GraphPad Prism 8. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
