Figure 9.
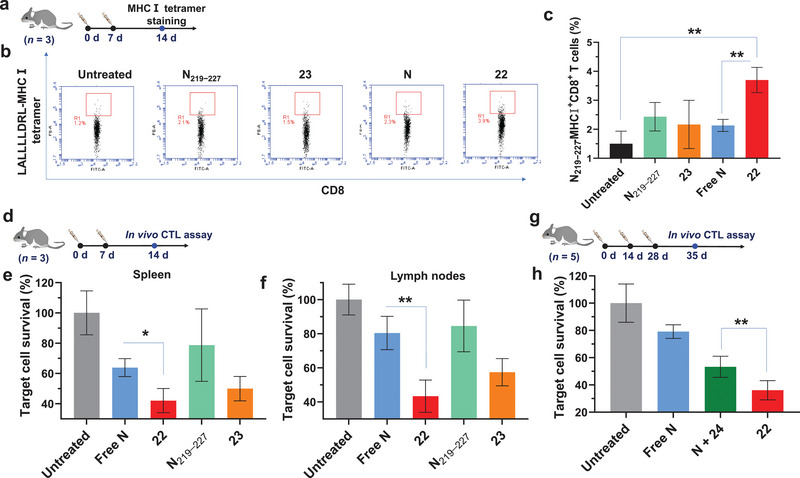
a–c) Vaccination of mice with TCCSia‐Ace‐Dex‐N‐Rd (22) induced N219−227 specific cytotoxic T‐lymphocytes (CTLs) in their splenocytes. C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously immunized on days 0 and 7 with free N (50 µg), N219−227 (equivalent to the amount of N219−227 in 50 µg N), 22 (with 50 µg N), or 23 (with the same amount of N219−227 as the N219−227 treated group). 14‐day later, their spleens were collected for MHC‐I tetramer staining. The percentage of LALLLLDRL‐MHC‐I+CD8+ cells present in splenocytes was determined by staining splenocytes with PE‐conjugated LALLLLDRL‐MHC‐I tetramer prepared by QuickSwitch Custom MHC Tetramer Kit and FITC‐conjugated anti‐mouse CD8 antibody. d–f) In vivo CTL activities of free N, N219−227, 22 and 23. By weekly injections, mice were immunized twice with free N (50 µg), N219−227 (equivalent to the amount of N219−227 in 50 µg N), 22 (with 50 µg N) or 23 (with the same amount of N219−227 as the N219−227 treated group), respectively, using nontreated mice as control (n = 3 mice per group). 14‐day later, a mixture of CFSEhiN219−227 + target cells and CFSEloN219−227 − control cells with a ratio of 1:1 was injected into the immunized and nontreated mice, respectively. One day after injection, e) their splenocytes and f) lymph node cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. g,h) Mice were immunized three times with free N (50 µg), 22 (with 50 µg N) or N + 24 (with 50 µg N), respectively (n = 5 mice per group). 35‐day later, in vivo CTL assay was performed. A two‐tailed unpaired Student's t‐test determined the p values with GraphPad Prism 8. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
