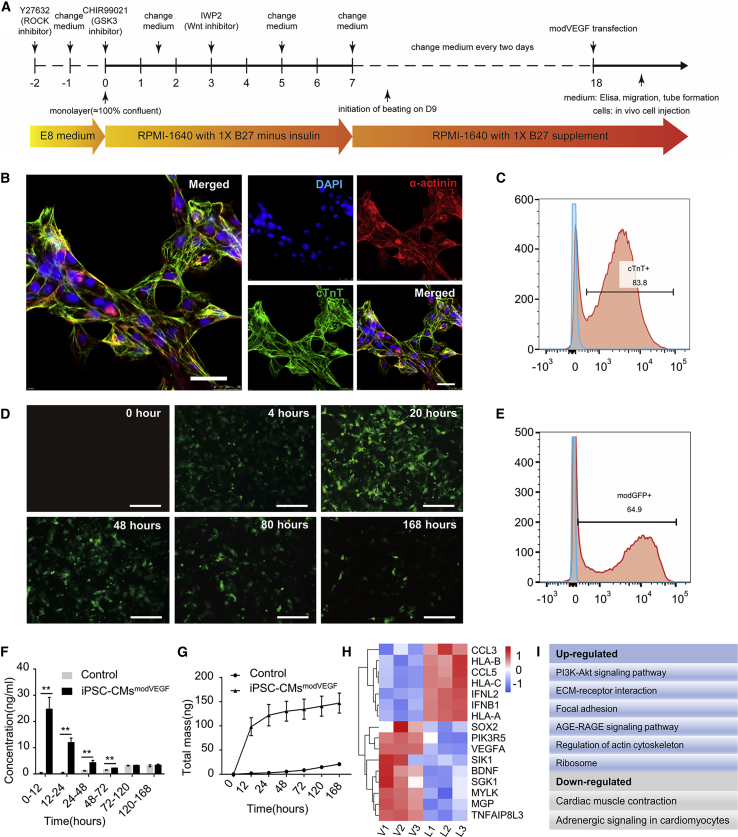
Figure 1.
Cardiac differentiation and characteristics of iPSC-CMs following modRNA transfection
(A) Schematic diagram of the protocol for CM differentiation from iPSCs. (B) Representative immunostaining images of CMs on day 18 of differentiation with myocardial structural markers cTnT, α-actinin. Scale bar, 25 μm. (C) Cardiac troponin expression on day 18 was analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 3). (D–G) Transfection efficiency and secretion kinetics of VEGF modRNA in iPSC-CMs. (D) Representative photomicrographs of CMs at 0, 4, 20, 48, 80, and 168 h post transfection with a modGFP reporter. Scale bar, 200 μm. (E) Representative flow cytometry analysis from modGFP-transfected iPSC-CMs at 20 h post transfection. (F and G) Kinetics of (F) newly produced and (G) cumulative VEGF protein concentration at denoted time points after transfection of modVEGF into iPSC-CMs. p values were determined by one-way analyses of variance followed by Bonferroni post test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. (H) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to growth and metabolism of iPSC-CMs; each rectangle represents one gene, blue indicates low-intensity expression, red indicates high-intensity expression. (I) KEGG pathway analysis reveals the most up/downregulated pathways (related to cell growth and metabolism), as a result to VEGF mRNA transfection in iPSC-CMs.