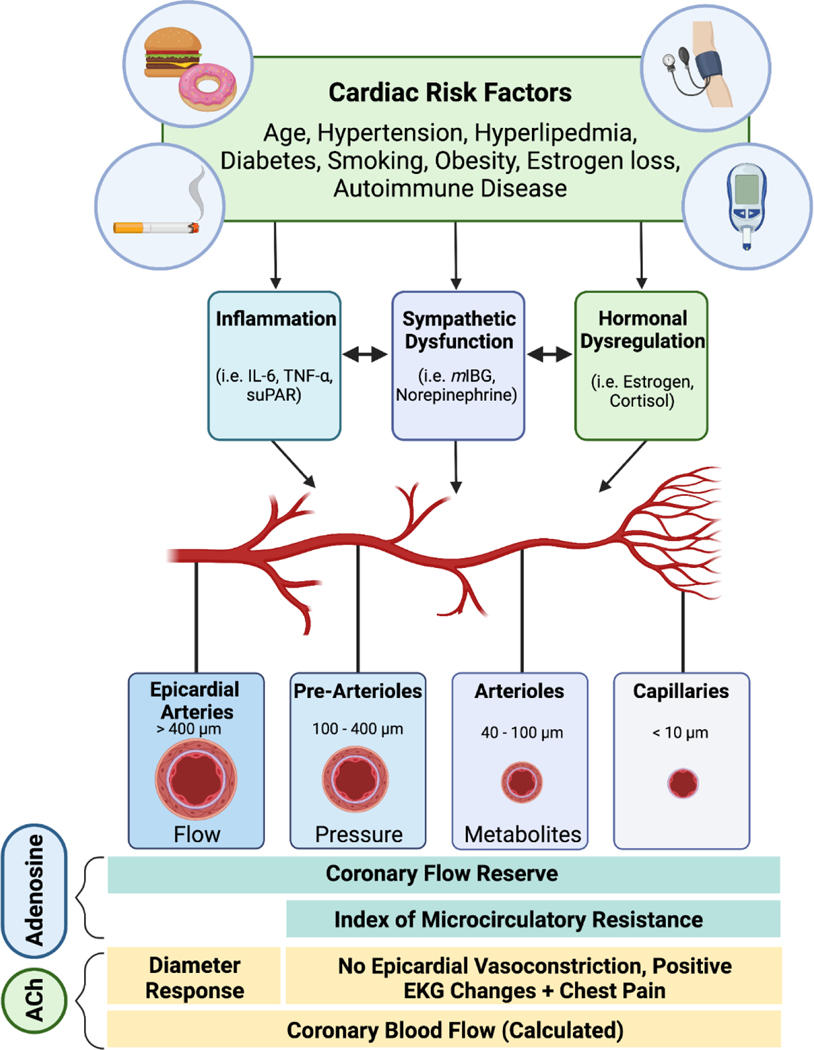
Figure 2.
Coronary vascular dysfunction.
Cardiac risk factors such as age, hypertension, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, smoking, obesity, menopause, and chronic autoimmune inflammatory disorders, lead to abnormal coronary vascular function (functional abnormalities as well as structural abnormalities from arteriolar remodeling) that impair myocardial blood flow and cause microvascular ischemia even in the absence of epicardial obstructive stenosis. The main stimulus for vascular reactivity varies along the coronary vascular tree depending on the vessel caliber and the surrounding myocardial matrix; for example, while changes in sheer stress and pressure stimulate periarteriolar vessels, the micro vessels are under metabolic control (pH, adenosine, hypoxia, K+, etc). Comprehensive coronary function testing using adenosine and acetylcholine interrogates coronary epicardial and microcirculatory function. Image created using Biorender.com.