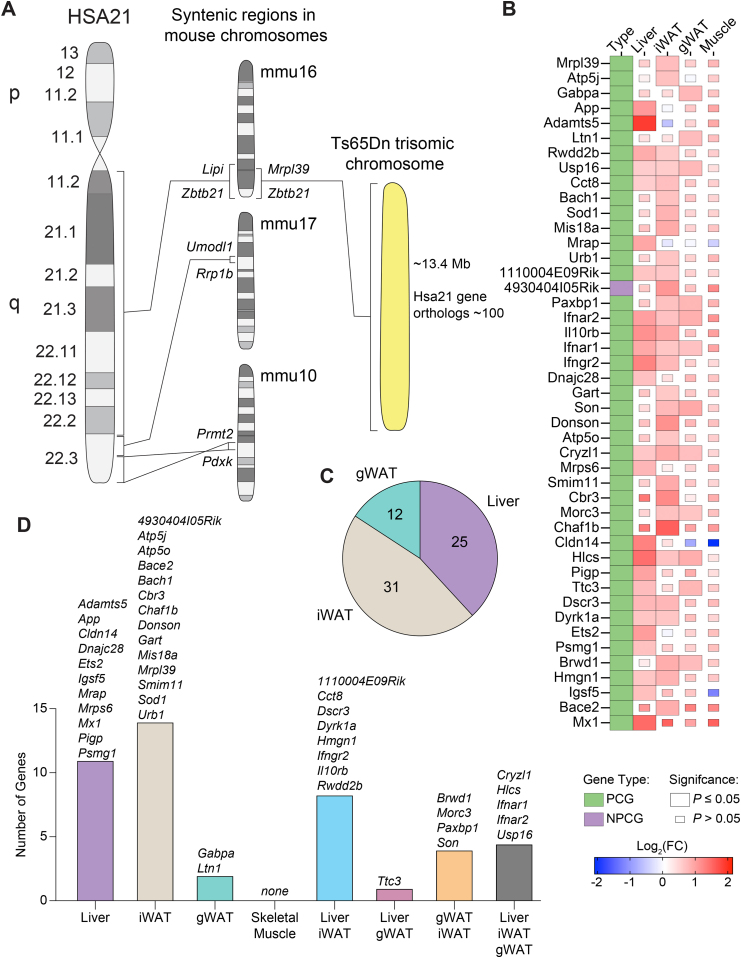
Figure 7.
Selective expression of trisomic genes in the adipose tissue, liver, and skeletal muscle of Ts65Dn mice. A) The orthologous genes on human chromosome 21 (Hsa21) are distributed across three syntenic segments located on mouse chromosomes Mmu10, Mmu16, and Mmu17. Ts65Dn mice are trisomic for ∼104 genes (from Mrpl39 to Zbtb21) out of ∼140 (Lipi to Zbtb21) on Mmu16 that are syntenic to Hsa21. B) Heat map of all trisomic genes in Ts65Dn mice fed a high-fat diet that are differentially expressed relative to euploid littermate controls by at least one tissue. Green box denotes protein coding gene (PCG) and purple box denotes non-protein coding gene (NPCG). The size of the box indicates statistical significance in trisomic gene expression between male Ts65Dn mice relative to euploid controls. Full-size box denotes significantly different expression (P ≤ 0.05), and small box size denotes non-significant expression between genotypes (P > 0.05). The color gradient indicates Log2 fold-change of each gene in Ts65Dn relative to euploid controls, with upregulated genes in the red and downregulated genes in the blue color spectrum. Tissue sample size for all RNA sequencing (Euploid, n = 6; Ts65Dn, n = 6). iWAT, inguinal white adipose tissue; gWAT, gonadal white adipose tissue. C) A pie chart indicating the number of trisomic genes significantly (P ≤ 0.05) and differentially (Log2(FC) ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 0.5) expressed in Ts65Dn mice relative to euploid controls by each tissue. None of the trisomic genes were differentially expressed in the skeletal muscle of Ts65Dn mice. D) Overlap analysis of trisomic genes significantly and differentially expressed by each tissue with lists of all genes contained in each group.