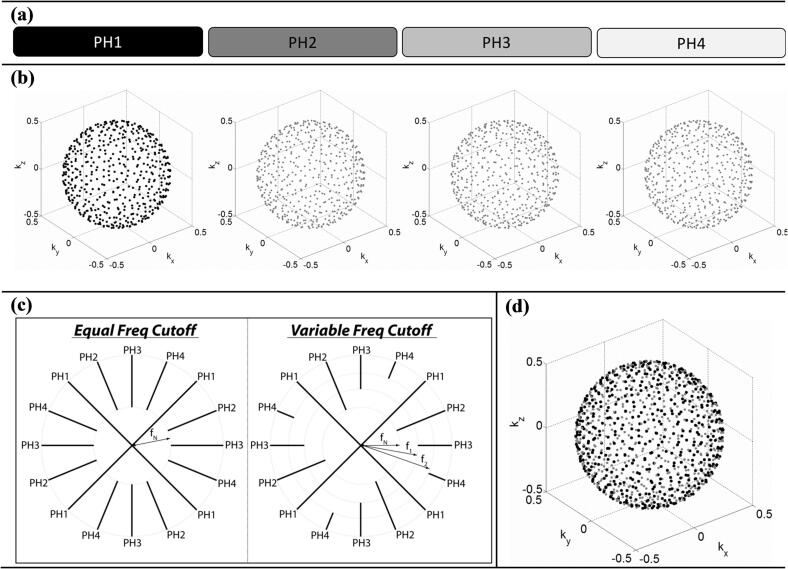
Fig. 1.
Sampling and reconstruction strategy for respiratory imaging with 4D-PEVS. (a) In this diagram, k-space data for each respiratory phase (PH) are represented by a rectangle (for clarity, respiratory cycle hypothetically divided into four phases). Grayscale intensity (black = all, white = none) illustrates the amount of respective k-space data used to reconstruct phase 1. (b) k-space sampling functions (for clarity, only end-point of radial spokes shown). MR data for each phase are acquired in a quasi-random distribution of non-overlapping k-space points. (c) An overview of PEVS filters (2D k-space shown). The periphery of k-space data from all phases may contribute equally to the reconstruction of phase 1 (equal frequency cutoff) or the contribution of k-space from neighboring phases can be reduced by varying the cutoff frequency (variable frequency cutoff). fN represents the radial distance in k-space below which the sampling rate is higher than that required by the Nyquist criterion. (d) Sampling function for reconstruction of phase 1; black represents the sampling points for phase 1 while gray represents the sampling points from all other phases.