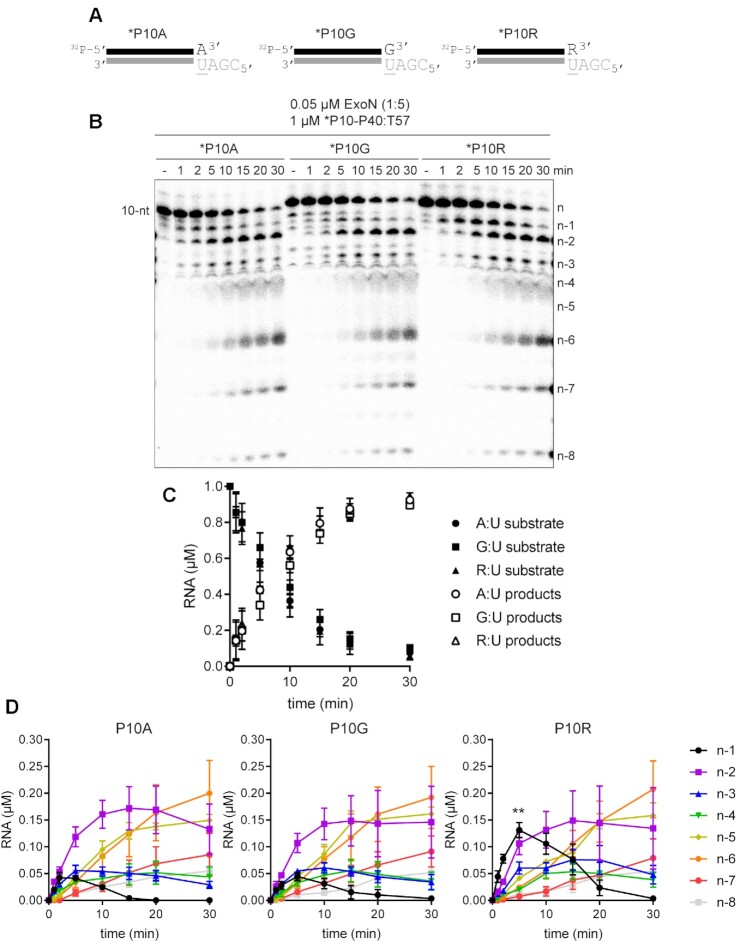
Figure 7.
Terminal basepair-dependent differences in the kinetics of hydrolysis by ExoN. (A) Schematic of dsRNA substrates used to evaluate the influence of the terminal basepair on kinetics of excision by ExoN. The termini have a A:U, G:U or R:U basepair, where R represents remdesivir. (B) Effect of terminal basepair on hydrolysis by ExoN. Reactions contained 0.05 μM ExoN (1:5) and 1 μM of the indicated dsRNA substrate, were incubated at 30°C for the indicated times, then quenched. Product analysis is shown. (C) Analysis of the kinetics of substrate utilization and product formation. Here, depletion of substrate and total product formation are monitored, showing no difference in the kinetics, error bars indicate mean ± SD (n = 3). (D) Analysis of the kinetics of formation of each individual product. Cleavage products (n – 1 to n – 8) were plotted as a function of time for each RNA substrate, error bars indicate mean ± SD (n = 3). The kinetics of formation and utilization of the n – 1 product vary between substrates, suggesting that some, but not all steps of the mechanism are agnostic to the sequence and/or complementarity of the terminal basepair. Statistical analysis (unpaired t-test) comparing the n – 1 products from P10A to P10R at 5 min is indicated, P = 0.0038.