Figure 8.
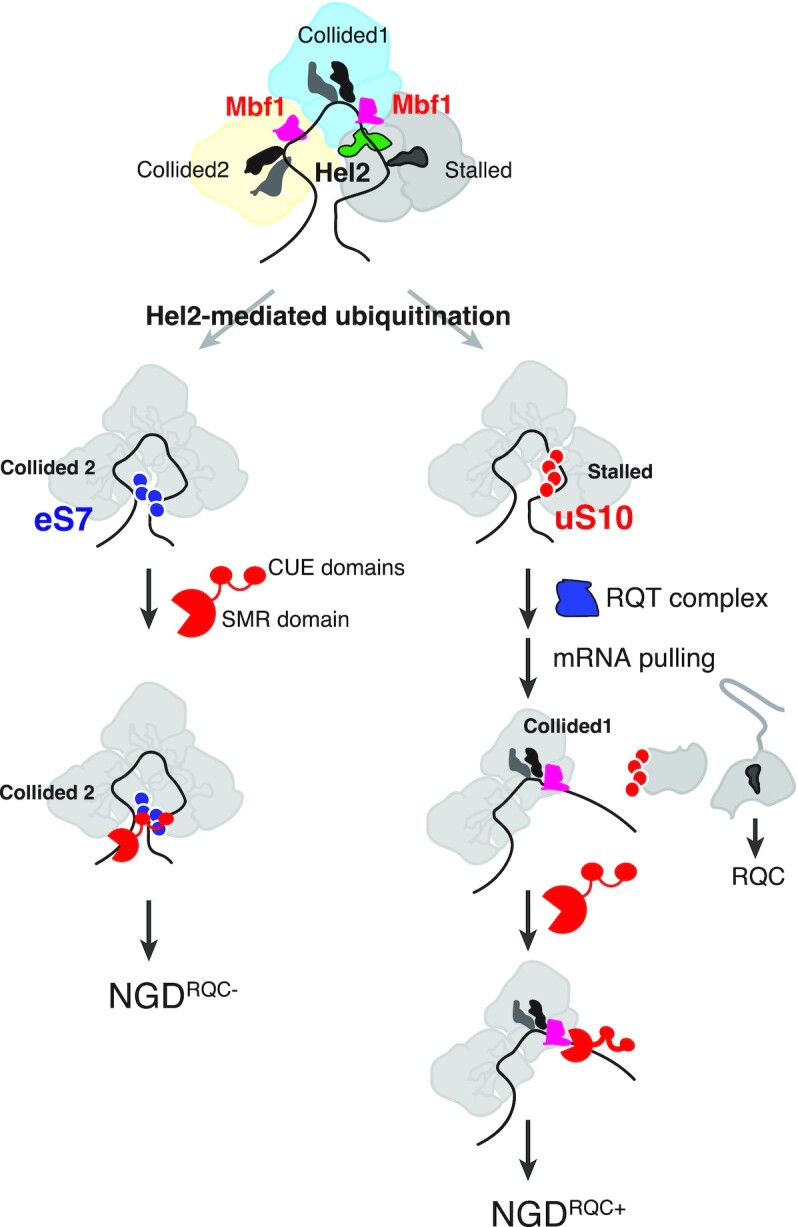
A model for the role of Cue2 in two modes of NGD. A model for Cue2 recognition of the substrates of two modes of NGD induced by the rare codon staller. A model for NGDRQC− (left): Hel2 forms K63-linked polyubiquitin chains on eS7 (shown in blue circles) of the colliding ribosome in the trisome formed on the SDD1 mRNA. Cue2 binds to the K63-linked polyubiquitin chains on eS7 with two CUE domains, CUE-D1 and CUE-D2. The Cue2 bound to the stalled ribosome cleaves the mRNA upstream of the colliding ribosome 2 (collided 2). A model for NGDRQC+ (right): Hel2 ubiquitinates uS10 on the leading ribosome and the RQT complex recognizes the polyubiquitinated uS10 (shown in red circles). The Slh1 helicase subunit of RQT applies a pulling force on the mRNA, leading to the dissociation of the leading ribosome into subunits. The collided ribosome 1 (collided 1) functions as a ram or giant wedge, but mRNA is partially released. After pulling of mRNA by the RQT complex, Cue2 cleaves mRNA partially released from the colliding ribosome 1.
