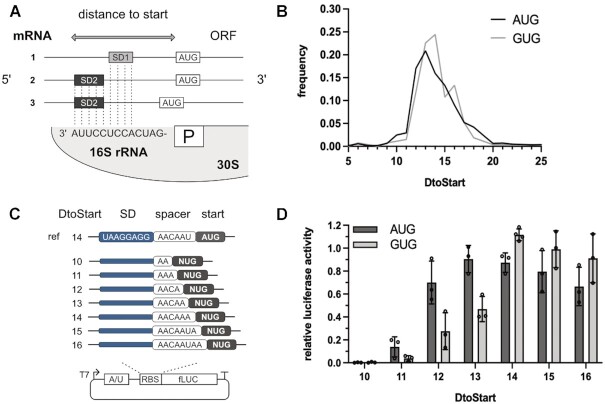
Figure 1.
The importance of aligned spacing for initiation efficiency. (A) Schematic depiction of a ribosomal binding site and the SD:aSD motif interaction. Different SD motifs can position the start codon (AUG) similarly in respect to the ribosomal P-site (P). Measuring the distance from the 3′ end of the 16S rRNA to the start codon of a hybridized mRNA provides a metric for aligned spacing termed distance to start (DtoStart). In the depicted example, mRNAs 1 and 2 share the same DtoStart, while the aligned spacing of mRNA 3 is shorter. (B) Genome-wide frequency distribution of aligned spacing (DtoStart) for SD-led E. coli genes with AUG (dark grey) or GUG (light grey) start codons. (C, D) To assess initiation efficiency in dependence of start codon identity and aligned spacing, S30 extract based luciferase reporter gene assays were carried out. (C) The firefly luciferase (fLUC) reporters with AUG or GUG start codons carried a strong SD motif and spacer sequences of varying lengths. The DtoStart of the luciferase genes ranged from 10 to 16 (spacer length 2 to 8 nts, respectively). (D) Luciferase activity depending on initiation at AUG and GUG is depicted in dark and light grey, respectively. The luminescent signal measured was related to the activity of a reference construct, carrying a distinct AUG start codon (ref). The mean and the standard deviation of the measurements are shown.