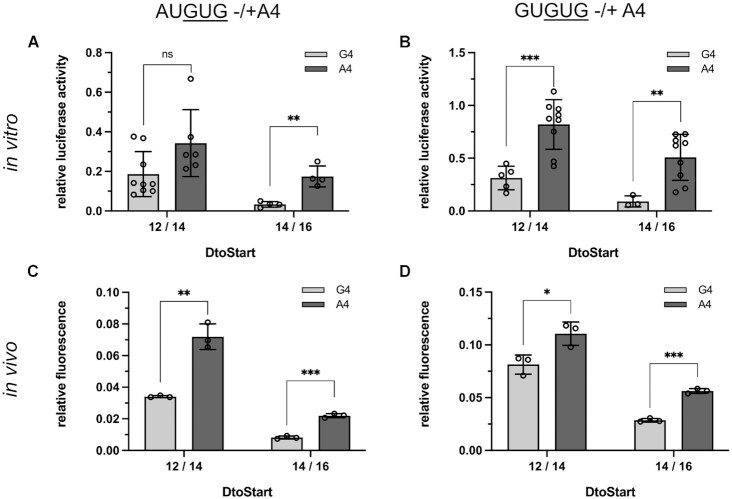
Figure 7.
Impact of A4 on start codon selection at AUGUG and GUGUG ambiguous sites. In vitro luciferase (A, B) and in vivo GFP (C, D) reporter assays were employed to determine a potential contribution of A4 to start codon selection at AUGUG (A, C) and GUGUG (B, D) initiation sites. Reporter gene expression was dependent on initiation at the 3′ GUG start codon in frame of the respective CDS. For both reporters, constructs were generated harboring either G4 (light grey) or A4 (dark grey). The RBSs were kept constant between the luciferase and GFP reporters and the impact of A4 on initiation efficiency was monitored at two aligned spacings (DtoStart 12/14 and 14/16), providing varying degrees of initiation ambiguity. Measured relative light units from the luciferase as well as normalized GFP fluorescent signal (GFP/OD700) were related to the signal obtained from reference constructs harboring a distinct AUG start codon. For both the in vitro (A, B) and in vivo data (C, D), the error bars indicate the standard deviation of the independent experiments. Statistical significance was tested, employing a two-tailed, unpaired t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).