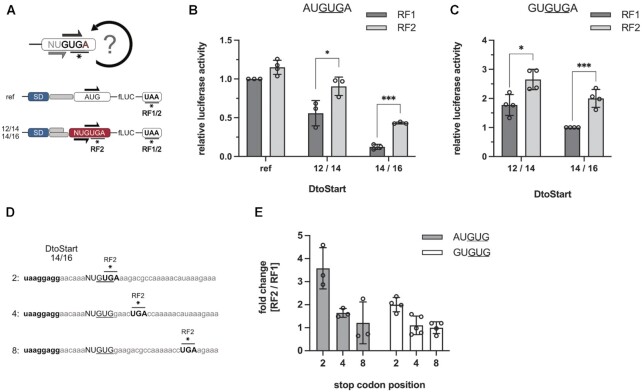
Figure 9.
RF2-dependent activity of luciferase constructs harboring AUGUGA or GUGUGA ambiguous initiation sites. (A) Experimental design to determine the contribution of RF2-dependent termination to start codon selection. mRNAs with the luciferase CDS in frame of the 3′ GUG within an AUGUGA and GUGUGA context and a DtoStart of 12/14 as well as 14/16 were in vitro translated in presence of RF1 or RF2. As a control, a reference mRNA (ref) was employed that harbored a distinct AUG start codon and thereby depended solely on the UAA stop codon of the luciferase CDS. Relative luciferase activities of the reporter mRNAs carrying AUGUGA (B) or GUGUGA (C) initiation sites in the presence of RF1 (dark grey) or RF2 (light grey) are shown. (D, E) Additionally, RF2 dependence was assessed as a function of the UGA stop codon position within the 5′ start codon-dependent ORF. The initiation and termination sequence context of the employed reporter mRNAs with DtoStart 14/16 are depicted in (D). The SD motifs as well as the UGA stop codons, located at different positions within the alternative 5′ start codon-dependent ORF, are indicated in bold. The fold changes of luciferase activities in presence of RF2 compared to RF1 are depicted for AUGUG (grey) and GUGUG (white) start sites in (E). The mean and the standard deviation are shown. Statistical significance was tested, employing a two-tailed, unpaired t-test. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).