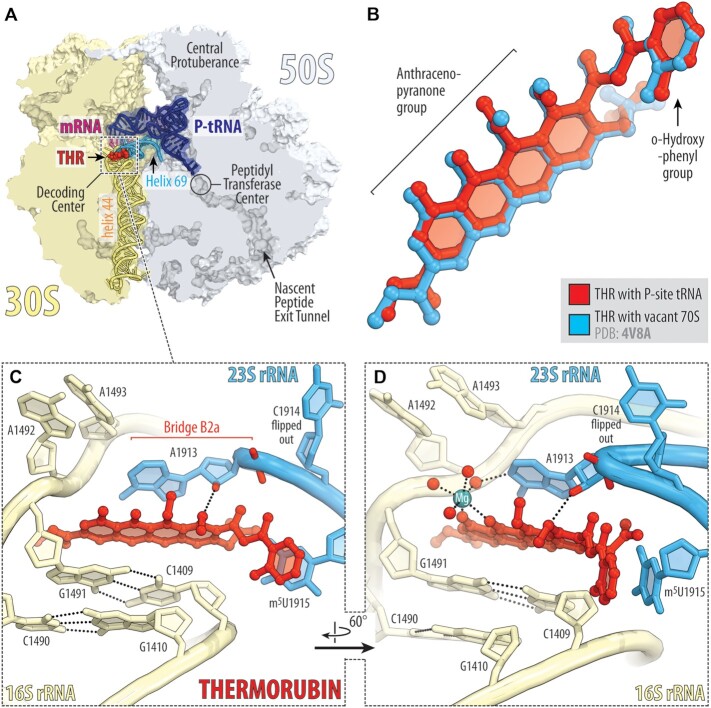
Figure 3.
X-ray crystal structure of 70S-THR complex with P-site tRNA. (A) Overview of the drug-binding site (red) in the T. thermophilus 70S ribosome carrying mRNA (magenta) and deacylated initiator tRNA in the P site (navy) viewed as a cross-cut section through the nascent peptide exit tunnel. The 30S subunit is shown in light yellow; the 50S subunit is light blue. Helices 69 and 44 of the 23S and 16S rRNAs are highlighted in blue and pale yellow, respectively. (B) Superposition of the ribosome-bound THR in the presence of P-site tRNA (red) with the previous structure of THR bound to a vacant ribosome (blue, PDB entry 4V8A (8)). The structures were aligned based on helix 44 of the 16S rRNA. (C, D) Close-up views of the THR bound in the decoding center of the 70S ribosome (E. coli numbering of the 23S and 16S rRNA nucleotides is used). Potential H-bond interactions are indicated with dashed lines. Note that binding of THR to the 16S–23S bridge B2a causes nucleotide C1914 to flip out of its usual location in the absence of A-site tRNA. Also note that THR binding, even with the empty A site, induces nucleotides A1492 and A1493 of the 16S rRNA to flip out of helix 44.