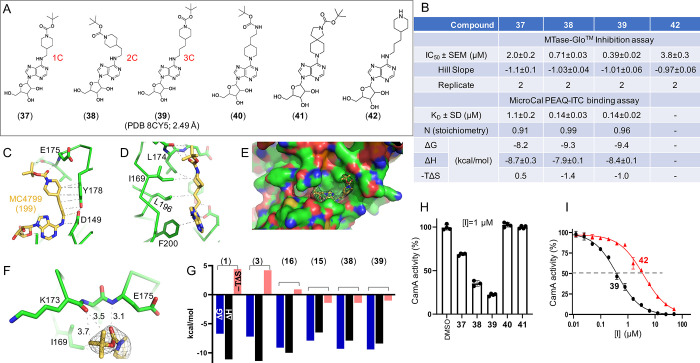
Figure 6.
Compound 39 is the most potent inhibitor of CamA tested to date. (A) Chemical structures of compounds 37–39 with varied carbon length from 1- to 3-carbon atoms and of the related compounds 40–42. (B) Summary of inhibition (IC50), dissociation constant (KD), and X-ray information (PDB). (C, D) Two views of compound 39 showing the extensive hydrophobic contacts (PDB 8CY5). (E) Surface presentation (green for carbons, red for oxygens, and blue for nitrogen atoms) showing the binding site of 39, superimposed with the omit electron density map (contoured at 5.0 σ above the man). Note that the sulfur atom of Cys65 is visible (colored in yellow, towards the lower left). (F) Compound 39 forms H-bonds with the main-chain amide nitrogen atom of E175 and main-chain carbonyl oxygen atom of Lys173 (PDB 8CY5). (G) Thermodynamic parameters derived from ITC measurements (free energy ΔG, binding enthalpy ΔH, and entropy −TΔS). (H) CamA inhibition of five related compounds (37–41) at [I] = 1 μM, in the presence of 40 μM SAM co-substrate. (I) Compound 42 (without carbamate moiety) has reduced inhibition potency.