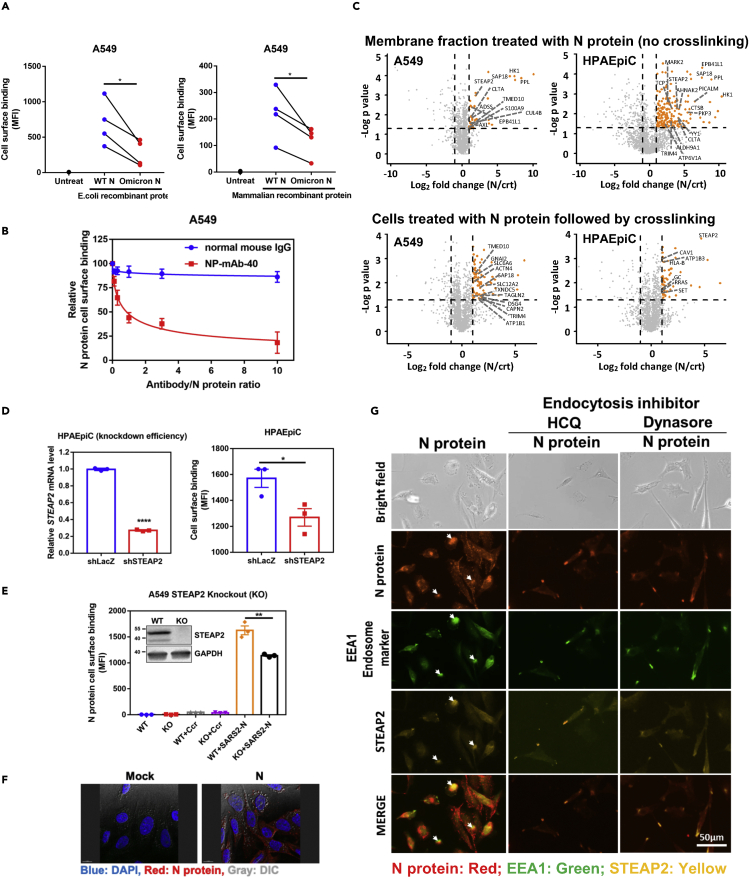
Figure 1.
N protein binds to and enters the cell through STEAP2
(A) Comparison of the cell-binding capacity of SARS-CoV-2 wild type (WT) N protein and Omicron N protein expressed in either E. coli or mammalian cells. 1 × 105 A549 cells were used to mixed with 1 μg WT N or Omicron N proteins. One hour after protein addition, allophycocyanin (APC) conjugated anti-His antibody was used to detect the cell binding capacity of WT N protein or Omicron N protein. The samples were analyzed by flow cytometry and data are shown as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI).
(B) Antibody blocking assay. Aliquots of 10 μg of SARS-CoV-2 N protein were pre-mixed with 0, 1, 3, 10, 30, and 100 μg of normal mouse IgG or anti-N monoclonal antibody (NP-mAb-40) and incubated at 4°C overnight. The antibody/N protein complex was used for the A549 cell surface binding assay. The blocking capacity of anti-N antibody was normalized to N protein only control.
(C) Membrane fractions of A549 and HPAEpiC cells were extracted and incubated with N protein conjugated beads for 3 h binding at 4°C, and pull-downed for LC-MS-MS analysis (upper panels). A549 and HPAEpiC cells were suspended and treated with N protein for 1 h on ice. After incubation, cells were crosslinked with 3 mM DTSSP for 1.5 h. Then, cells were lysed in RIPA lysis buffer, and N protein complex in the lysate was immunoprecipitated for LC-MS-MS analysis (lower panels). Y axis denotes −logP values while the X axis shows log2 fold change values. Orange dots highlight the statistically significant proteins, with p value < 0.05 (-Log p > 1.3) and fold change>2, and the enriched plasma membrane protein was labeled on the plot. Identified proteins were further sorted by HuMemProtDB.
(D) To knock-down (KD) STEAP2 expression, HPAEpiC cells were infected with lentivirus carrying STEAP2 shRNA followed by puromycin selection for 14 days. The STEAP2 mRNA expression levels were assessed by qRT-PCR, and the relative KD efficiency of shSTEAP2 was compared to shLacZ control (left-hand side panel). N protein binding capabilities to HPAEpiC STEAP2 KD cells and shLacZ control KD cells were assessed by flow cytometry analysis, and data were shown as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). (right-hand side panel).
(E) Western blot analysis of STEAP2 in wild type (WT) and knock-out (KO) A549 cells were shown. N protein binding to A549 STEAP2 KO cells was assessed by flow cytometry analysis and shown as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Ccr (crotonyl-CoAcarboxylase/reductase, a bacterial protein) binding was used as a control.
(F) SARS-CoV-2 N protein enters alveolar cells. HPAEpiC cells were treated with 10 μg SARS-CoV-2 N protein overnight and then stained with anti-N antibody. The localization of N protein (Red) was checked by fluorescence microscope and cell morphology was observed by dimensional interference contrast (DIC). Nuclei of cells were stained by DAPI (blue).
(G) N protein entering cells by endocytosis and N protein co-localization with STEAP2. HPAEpiC alveolar cells were seeded on 8 well slides. Cells were pretreated with endocytosis inhibitors HCQ, or Dynasore. Then the cells were treated with N protein overnight. After treatment, the cells were stained by specific antibodies to detected N protein (red), endosome marker (EEA1) (green), and STEAP2 (yellow). Cells were observed under fluorescent microscopy (Invitrogen tech.). Scale bar: 50 μm. All data are shown as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; t test. See also Figure S5.