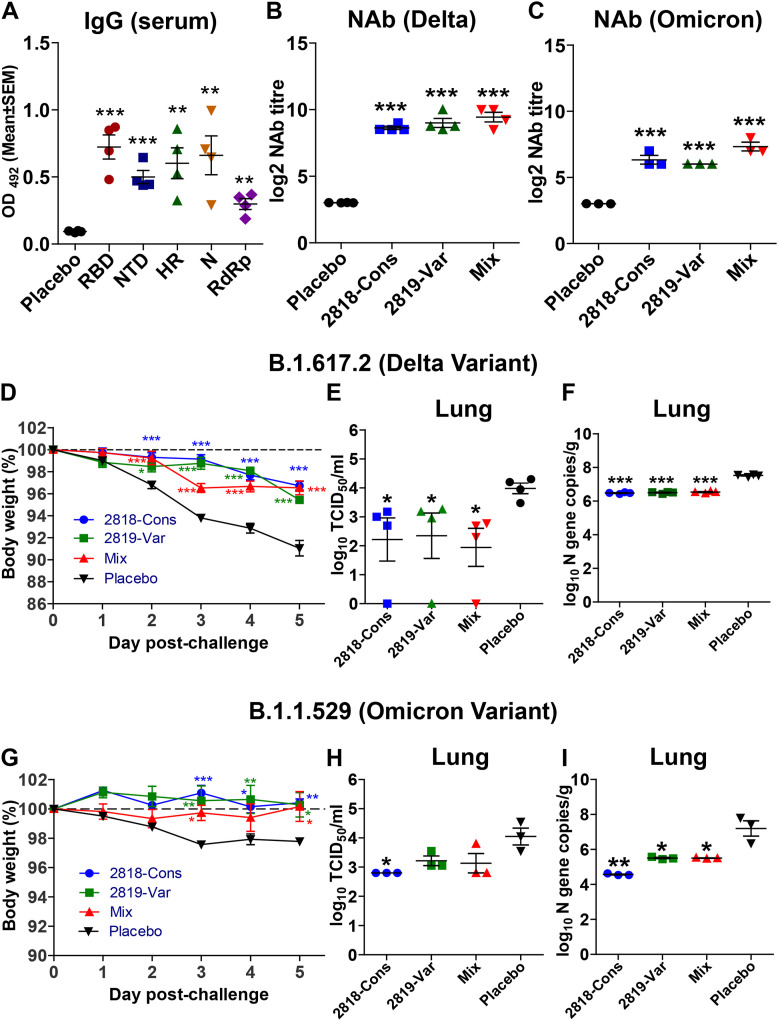
Fig. 5.
Humoral immune response and protection efficacy evaluation by the vaccines in hamster model. Syrian hamsters were immunized with 2 doses of 2 × 108 CFU and IgG and neutralizing antibody titre were assessed 3 weeks post-immunization. (A) IgG response in sera of hamsters on individual antigens. (B) Neutralizing antibody titre (NAb) quantified by CPE and IFA analysis against SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant. (C) NAb quantified by CPE and IFA analysis against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. To evaluate the protection conferred by the vaccine in a hamster model, Syrian hamsters were immunized orally with 2 doses of 2 × 108 CFU at a 2-week interval. 3 weeks post-immunization, hamsters were intranasally inoculated with 1 × 104 PFU of either the delta variant or omicron variant. (D) Percentage body weight change of hamsters after viral challenge with Delta variant. (E) Lung viral burden in Delta-challenged hamsters quantified by qPCR detection of SARS-CoV2 N gene. (F) Lung viral burden in Delta-challenged hamsters measured by TCID50. (G) Percentage body weight change of hamsters after viral challenge with Omicron variant. (H) Lung viral burden in Omicron-challenged hamsters quantified by qPCR detection of SARS-CoV2 N gene. (I) Lung viral burden in Omicron-challenged hamsters measured by TCID50. Data were presented as log10 TCID50 and log10-transformed viral N gene copies/g. Data were analysed by independent-samples T-test and ANOVA. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001.