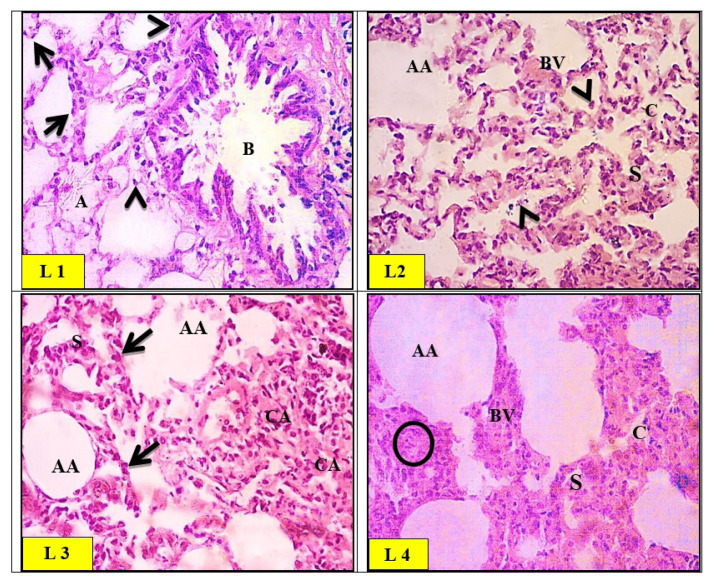
Fig. 9.
Light micrographs of control (L1) group of rat lung showing a normal histological appearance of the alveolar tissue with patent alveoli (A) and thin inter-alveolar septa. High power view of the control rat alveolar tissue revealed pneumocytes type I (arrows) and type II (arrowheads). A bronchiole (B) with folded epithelium was also noticed. Light micrographs of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-nps) (L2) group of rat lung showed the interalveolar septa appearing thickened with an area of destruction and extruded cells into the alveolar lumina (arrowheads). Few foci exhibited emphysematous changes and destructed septa (AA). Congested blood vessels (BV) were also seen. Light micrographs of aluminum oxide nanoparticles (Al2O3-nps) (L3) group of rat lung showed alternation with areas of collapsed alveoli (CA) and thick interalveolar septa (S). Several areas demonstrated emphysematous changes with collapsed alveoli and ruptured walls (AA). Pyknotic nuclei of degenerated cells in the interalveolar septa were noticed (Arrows). Light micrographs of the combination (ZnO-nps + Al2O3-nps) (L4) group of rat lungs showed severe cellular infiltration (circles) and congested blood vessels (BV) as compared to the control group. Some alveoli revealed emphysematous changes (AA), and others were collapsed (CA). Areas of hyalinization and vacuolation are depicted within the thickened interalveolar septa (S) (H&E stain. Microscopic magnification ×400).