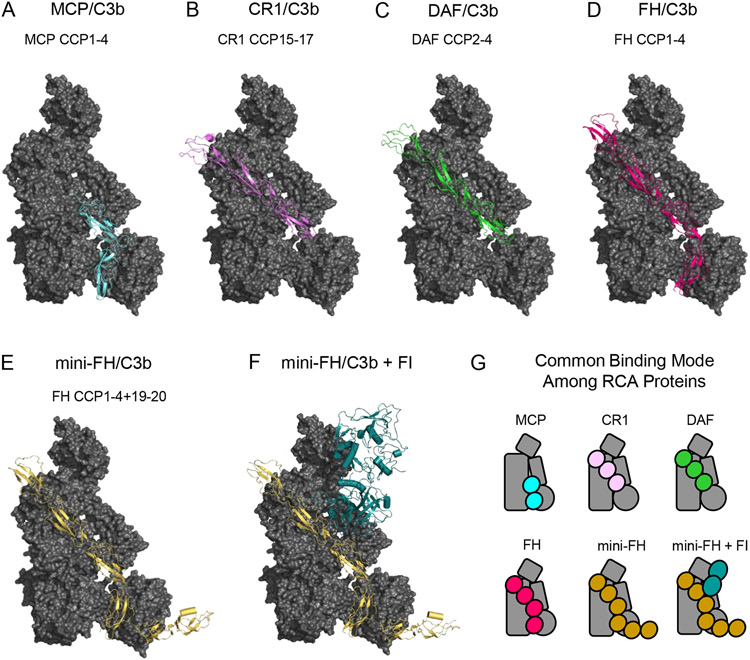
Figure 3.
Structural Features of C3b-binding Complement Regulatory Molecules. (A) Structure of C3b bound to CCP domains 1-4 of Membrane Cofactor Protein (MCP) as drawn from PDB entry 5FO8 [43]. C3b is colored as a grey surface, while MCP is colored light blue. (B) Structure of C3b bound to CCP domains 15-17 of Complement Receptor 1 (CR1) as drawn from PDB entry 5FO9 [43]. C3b is colored as a grey surface, while CR1 is colored pink. (C) Structure of C3b bound to CCP domains 2-4 of Decay Accelerating Factor (DAF) as drawn from PDB entry 5FOA [43]. C3b is colored as a grey surface, while DAF is colored green. (D) Structure of C3b bound to CCP domains 1-4 of Complement Factor H (FH) as drawn from PDB entry 2WII [44]. C3b is colored as a grey surface, while FH is colored magenta. (E) Structure of C3b bound to CCP domains 1-4 and 19-20 of mini-FH as drawn from PDB entry 5O32 [46]. C3b is colored as a grey surface, while mini-FH is colored gold. (F) Structure of C3b bound to mini-FH and Complement FI as drawn from PDB entry 5O35 [46]. C3b and mini-FH appear identically to panel E, while FI is colored dark blue. (G) Simplified representations of the structures shown in panels A-F. Note the common binding surface recognized by each of these C3b-binding regulatory molecules.