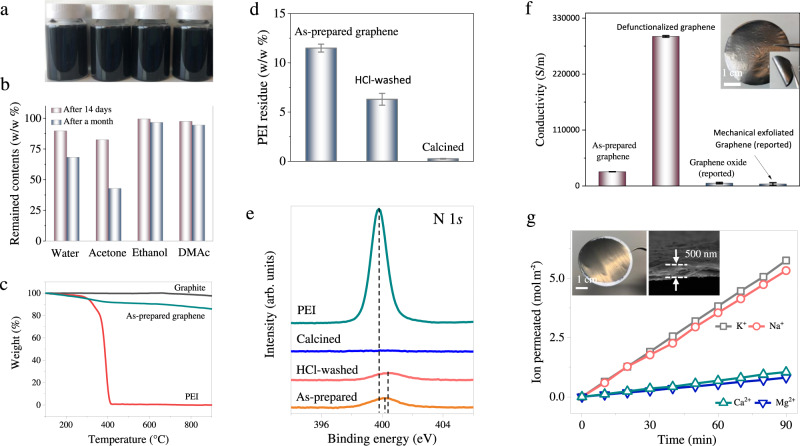
Fig. 2. Properties and potential applications of the exfoliated graphene nanosheets.
a Photograph of graphene nanosheets (10 h milling) dispersed in solvents including water, ethanol, isopropanol (IPA) and dimethylacetamide (DMAc) at a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL. b The weight ratio of remained graphene nanosheets in these solutions after fortnight and 30 days, respectively. c Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of graphite, polyethyleneimine (PEI) and exfoliated graphene (10 h milling), respectively. d Content of residual PEI on as-prepared graphene (10 h milling) and de-functionalized graphene by acid washing and incineration under N2 atmosphere. e High-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectra of N 1s of PEI, as-prepared graphene and de-functionalized graphene. The dashed lines highlight the peak shifts. In pure PEI, a sharp peak at 399.8 eV was recognized as typical groups of -N/NH/NH2 in PEI. A weak and broad N 1s peak also appears in exfoliated graphene but with a ~0.4 eV positive shift which might be caused by electron transfer from the polymer chains of PEI to graphene41. After HCl-treatment, the N 1s peak tends to be weaker and has more shift in comparison to pristine graphene, meaning fewer nitrogen remained and greater electron transfer between PEI and graphene. f The conductivity of the as-prepared graphene and defunctionalized graphene in comparison with reported graphene oxide and sonication exfoliated graphene. Inset is the photograph of the graphene film. g The permeation rate of monovalent ions (K+ and Na+) and divalent ions (Mg2+ and Ca2+) as a function of diffusion time in laminar membrane assembled using graphene nanosheets, inset are the photograph and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) cross-section image of the graphene membrane. All error bars indicate the standard deviation of the experiments.