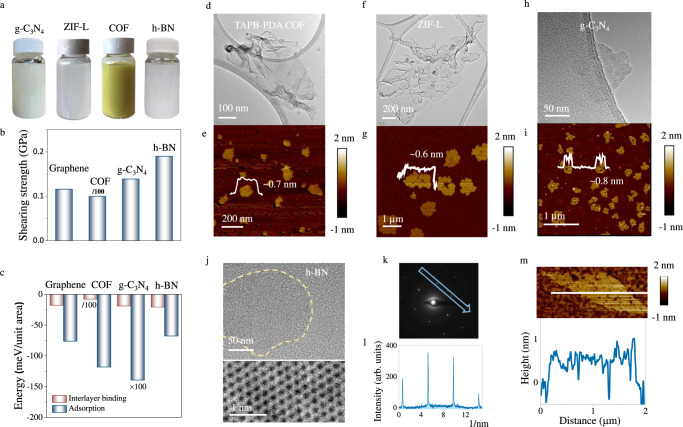
Fig. 4. Exfoliation of other layered materials by sticky milling.
a Photographs of exfoliated graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4), TAPB-PDA covalent organic framework (COF) and hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) nanosheets dispersed in water at a concentration of 1 mg/mL. Zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-L) nanosheets were dispersed in ethanol at a concentration of 1 mg/mL. b Comparison of the maximum interface shearing strength of graphene, TAPB-PDA COF, g-C3N4, and h-BN along the preferential sliding direction based on DFT calculation. Noted that the value for COF is multiplied by 100 to make it readable in this figure. This figure is based on the data from Supplementary Table 5.2. ZIF-L nanosheet was not studied by DFT calculation due to its structural instability (Supplementary Section 6.1.2). c Comparison of interlayer binding energy of studied materials (Graphene, TAPB-PDA COF, g-C3N4, and h-BN) and the adsorption energy of PEI on their surface. To make them readable, we multiplied the value of the binding energy of TAPB-PDA COF by 100 and divided the value of the adsorption energy of PEI/ g-C3N4 by 100. This figure is based on the data from Supplementary Table 5.1. Selected TEM and AFM image of the exfoliated d, e TAPB-PDA COF, f, g ZIF-L, h, i g-C3N4. Insets are the height profiles of the nanosheets. j Selected low and atomic-resolution TEM images of the exfoliated BN nanosheets. k Selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of a monolayer h-BN. l The intensity scan of the spots along the arrow in (k). m Selected AFM image and height profile of a single-layer h-BN.