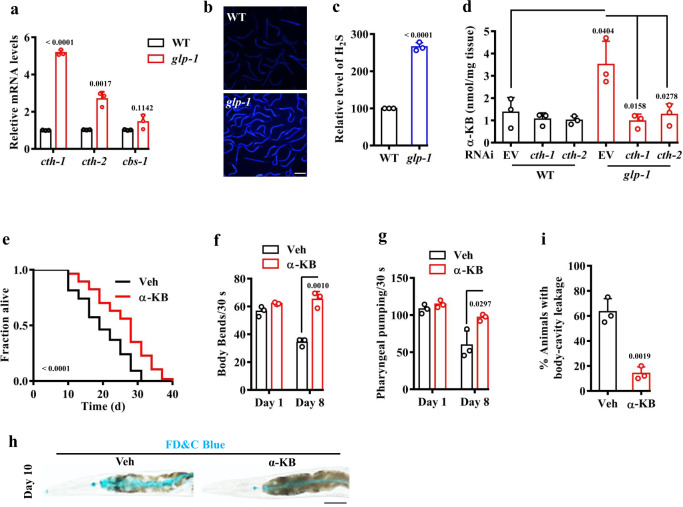
Fig. 1. Alpha-KB promotes lifespan in worms.
a The mRNA levels of cth-1 and cth-2, but not cbs-1, were upregulated in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, compared with those in wild-type (WT) worms. These results are means ± SD of three independent experiments. b, c Representative images of H2S formation detected by a fluorescent probe. A similar pattern of H2S formation was observed in three independent experiments. Scale bars: 500 μm. c Quantification of fluorescent intensity in b. The content of H2S was increased in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, compared with that in WT worms. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 35 worms per experiment). P values (a, c) were calculated using the two-sample t-test. d The levels of α-ketobutyrate (α-KB) were increased in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, compared with that in WT worms. RNAi knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 reduced the contents of α-KB in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants back to those of WT worms. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments. e Supplementation with α-KB (500 μM) extended lifespan in WT worms. Veh vehicle. P value was calculated using a log-rank test. See survival statistics in Supplementary Data 1. f–i Supplementation with α-KB delayed the appearance of the aging markers, including pharyngeal pumping (f), body bending (g), and body-cavity leakages (h, i) in WT worms. Scale bars: 500 μm. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 25 worms per experiment). P values (d, f, g, i) were calculated using a one-way ANOVA followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.