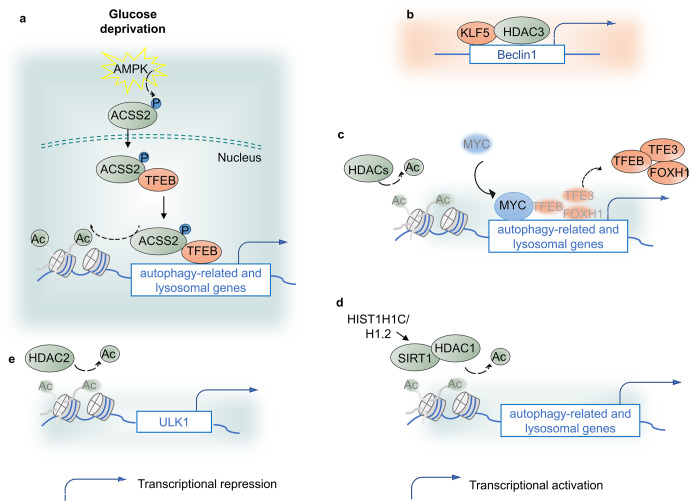
Fig. 3.
Histone acetylation and autophagy regulation. a Glucose deprivation assists AMPK-mediated ACSS2 phosphorylation and promotes its nuclear localization. In the nucleus, ACSS2 binds to TFEB and translocates to lysosomal and autophagy gene promoters, where ACSS2 generates acetyl-CoA for histone H3 acetylation and gene expression. b KLF5 protein and HDAC3 bind to the Beclin1 gene promoter and suppress its transcription, leading to autophagy suppression. c Coupled with MYC, HDACs, especially class I HDACs, epigenetically negatively regulate autophagic and lysosomal function. d HIST1H1C/H1.2 upregulates SIRT1 and HDAC1 to maintain the deacetylation of H4K16, leads to ATG proteins expression and then promotes autophagy, inflammation and cell toxicity. e Small-chain fatty acids treatment-reduced HDAC2 upregulates H3K27ac on ULK1 promoter, reduces ULK1 expression and autophagy flux and thus alleviate diabetic renal fibrosis