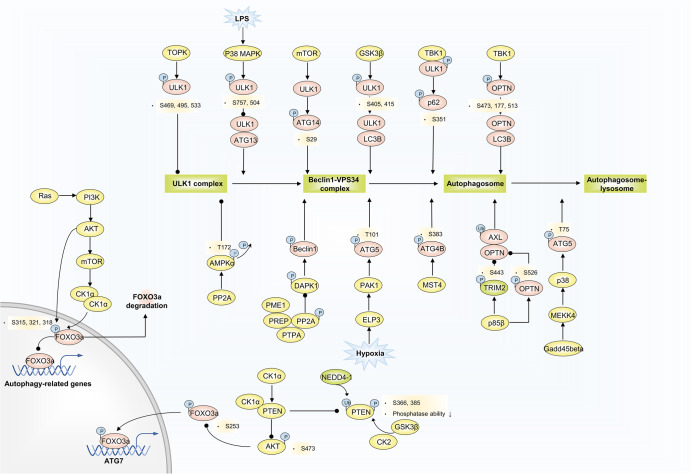
Fig. 7.
Phosphorylation and autophagy regulation. TOPK phosphorylates ULK1 at Ser469, Ser495, and Ser533, decreasing ULK1 activity and stability. LPS-activated p38 MAPK phosphorylates ULK1 at S757 and S504, preventing it from binding to ATG13, and reduced autophagy in microglia. GS3Kβ phosphorylates ULK1 at S405 and S415 sites, and thus promotes ULK1 and LC3B interaction. Activated ULK1 phosphorylates p62 and ATG14 to accelerate autophagy flux. Gadd45beta-MEKK4 pathway specifically directs p38 to autophagosomes, and p38 catalyzes phosphorylation of ATG5 at T75, resulting in an accumulation of autophagosomes through inhibition of lysosome fusion. ELP3 enhances PAK1 activity, thereby leading to ATG5 phosphorylation at T101. ATG4B is a direct MST4 substrate. MST4 phosphorylates ATG4B at S383 and contributes to increased autophagy activity. TRIM2 selectively ubiquitinates AXL to promote its autophagic degradation due to OPTN binding to the polyubiquitin chain of AXL. p85β mediates the phosphorylation of TRIM2 at the S443 residue and OPTN at S526, contributing to inhibited AXL degradation. Ras/PI3K/AKT/mTOR/CK1α/FOXO3 pathway limits an autophagy flux. CK1α/PTEN/AKT/FOXO3/ATG7 route excites autophagy. Polyubiquitination catalyzed by NEDD4-1 and phosphorylation by GSK3β and CK2 at the PTEN C-terminal reduce PTEN protein stability and inactivate phosphatase activity, activated PTEN blocks AKT phosphorylation at S473, subsequently inducing activated FOXO3a phosphorylation at S253. PP2A-DAPK1-Beclin1 and PP2A-AMPKα phosphorylation signaling pathways are involved in disease-related autophagy regulation