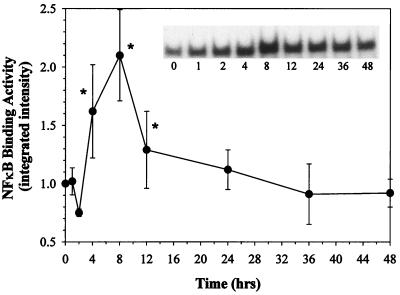
FIG. 4.
Treatment of human fibroblasts with glucan phosphate (1 μg/ml) results in a time-dependent increase in NF-κB nuclear binding activity. The data are shown as a graph of normalized integrated intensity. A representative gel shift assay is shown in the inset. The density (integrated intensity) of the band is directly proportional to the degree of NF-κB nuclear binding and activity. The time is given below each lane in the gel. The gels are quantified by computer-assisted scanning density, and the data are presented as means ± standard errors, with an n value of 3 per time point. The data are normalized to the zero time point value, which was set at 1.0. ∗, P < 0.05.