FIGURE 1.
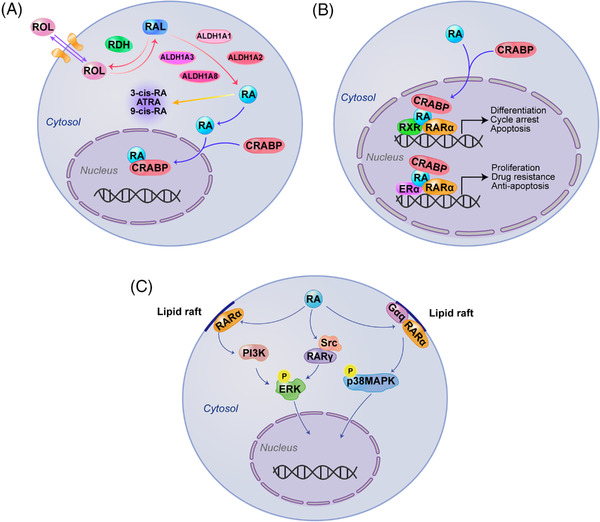
Aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDHs) in retinoic acid (RA) signaling. (A) When retinols (ROLs) are absorbed by cells and reversibly oxidized to retinaldehydes (RALs) by retinol dehydrogenases (RDHs). Specific ALDH isozymes (ALDH1A1, ALDH1A2, ALDH1A3, and ALDH8A1) then catalyze the irreversibly nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+)‐dependent oxidation of RALs to all‐trans RA (atRA), 9‐cis‐RA, and 13‐cis‐RA. (B) CRABPII transports RA to the nucleus where RA binds and activates heterodimers of nuclear RA receptors (RARs) or estrogen receptor α (ERα), respectively, on the RA response element (RARE), which can induce the transcriptional activity of target genes. (C) In response to RA, RARα translocates to lipid rafts in the cell membrane and interacts with Gαq proteins to activate the p38 mitogen‐activated kinase (p38MAPK) pathway. Besides, RARα and RARγ, via interaction with phosphoinositide 3‐kinase (PI3K) and non‐receptor tyrosine kinase (Src), respectively, can induce extracellular regulated–protein kinase (ERK) activation
