FIGURE 2.
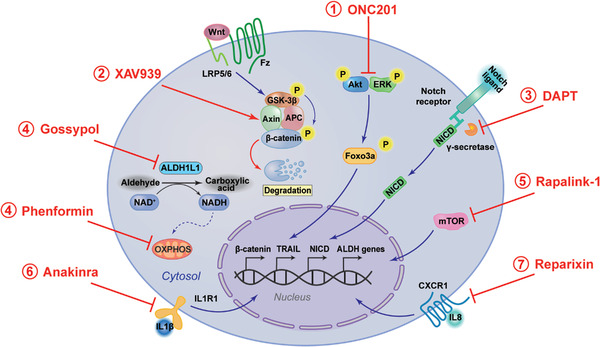
Therapies targeting aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDHs)‐related molecular pathways. (1) ONC201 dually inhibits phosphorylation of Akt and extracellular regulated–protein kinase (ERK), leading to the dephosphorylation of transcription factor Foxo3a. Dephosphorylated Foxo3a translocates into the nucleus where it activates transcription of its target genes, including pro‐apoptotic death receptor ligand TNF‐related apoptosis‐inducing ligand (TRAIL), ALDH1A1, and ALDH7A1. (2) WNT signaling inhibitor, XAV939 stimulates β‐catenin destruction by stabilizing Axin, which finally leading to significant inhibition of the ALDH‐positive populations. (3) Pharmacological inhibition of Notch pathway by using a γ‐secretase inhibitor, DAPT reduces ALDH‐positive tumor cells. (4) Dual inhibition of ALDH1L1 and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) by gossypol and phenformin reduces tumor bioenergetics and stemness. (5) Rapalink‐1 can block mTORC1/2 signaling and reduce ALDH‐positive populations. (6) IL‐1 receptor (IL1R1) antagonist, anakinra can decrease ALDH and IL1R1 double positive cancer stem cells (CSCs). (7) Reparixin can reduce the metastatic behavior of cancer cells and eradicate the ALDH‐positive populations by inhibiting IL8‐CXCR1 signaling
