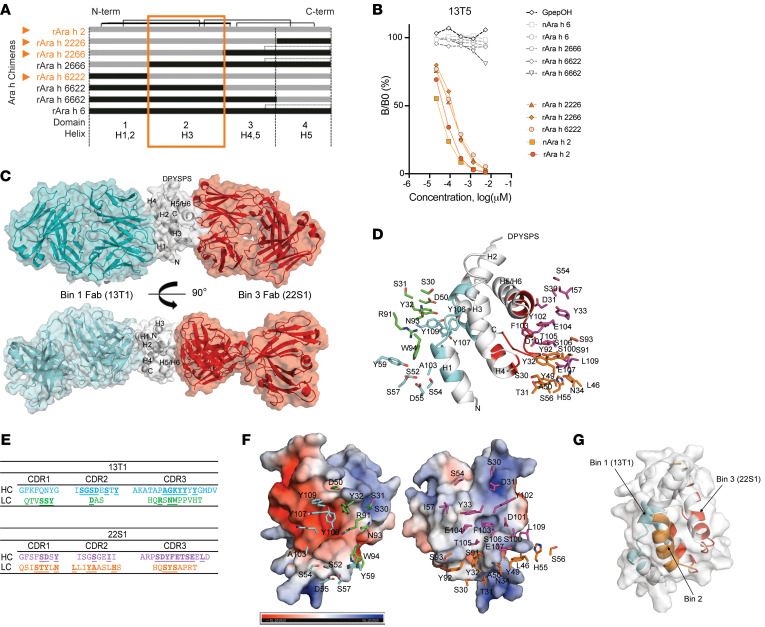
Figure 3. Definition of Ara h 2 conformational epitopes.
(A) Schema of Ara h 2 and Ara h 6 chimeras used in a (B) competitive inhibition ELISA assay to evaluate binding to the mAb 13T5 (orange represents the Ara h 2 domain 2 containing chimeras). The chimera name denotes Ara h 2 or Ara h 6 α-helices that the chimera contains in domain positions 1–4. (C) Overall arrangement of the ternary complex with bin 1 Fab (13T1, cyan), bin 2 Fab (22S1, red), and Ara h 2 (white) by x-ray crystallography. (D and E) Paratope residues interacting with Ara h 2 at the interface. The heavy and light chain carbons of 13T1 are shown in cyan and green; 22S1 heavy and light chain carbons are depicted in magenta and orange, respectively. Interacting residues are underlined. (F) Electrostatic surface properties of Ara h2 demonstrating Y106 (13T1) and F103 (22S1) packing against negative and positive pockets, respectively (related to Supplemental Table 3). Heavy and light chain carbons are colored as in E. (G) Ribbon representation of the 3 conformational epitopes of Ara h 2 (cyan shading for 13T1 bin 1, orange shading for bin 2, and red shading for 22S1 bin 3), with gray surface representation.