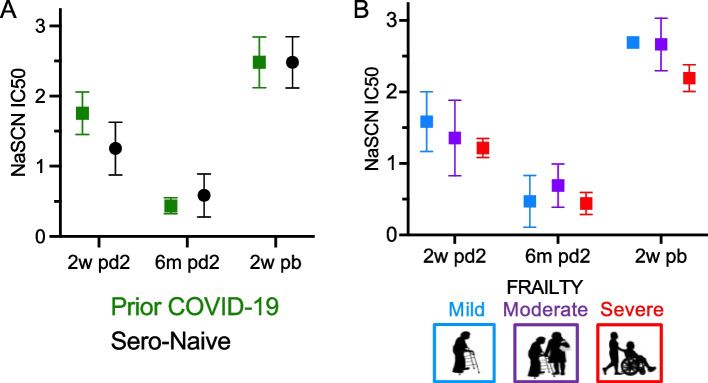
Fig. 3.
COVID-19 Vaccine Avidity Response in Frail Older Adults. ELISA was performed on patient samples for antibodies to spike IgG and RBD IgG over the study time course. Represented data points are: 2-weeks post vaccine dose 2 (2w pd2), 6-months post vaccine dose 2 (6 m pd2), and 2-weeks post booster vaccine (2w pb). (A&B) After 2 doses of vaccines (from 2w pd2 through 6 m pd2) avidity decreased in all study participants (p < 0.001). After the booster vaccine avidity improved in all participants above vaccine dose 2 levels (p < 0.001). (A) Individuals with prior COVID-19 infection had higher overall avidity response than uninfected (Sero-Naïve) (p < 0.001). After the boost, the impact of prior infection was non-significant (p = 0.88). Less frail individuals had higher avidity antibody over the study time course (p = 0.001). After the boost, the impact of frailty was no longer significant (p = 0.15)