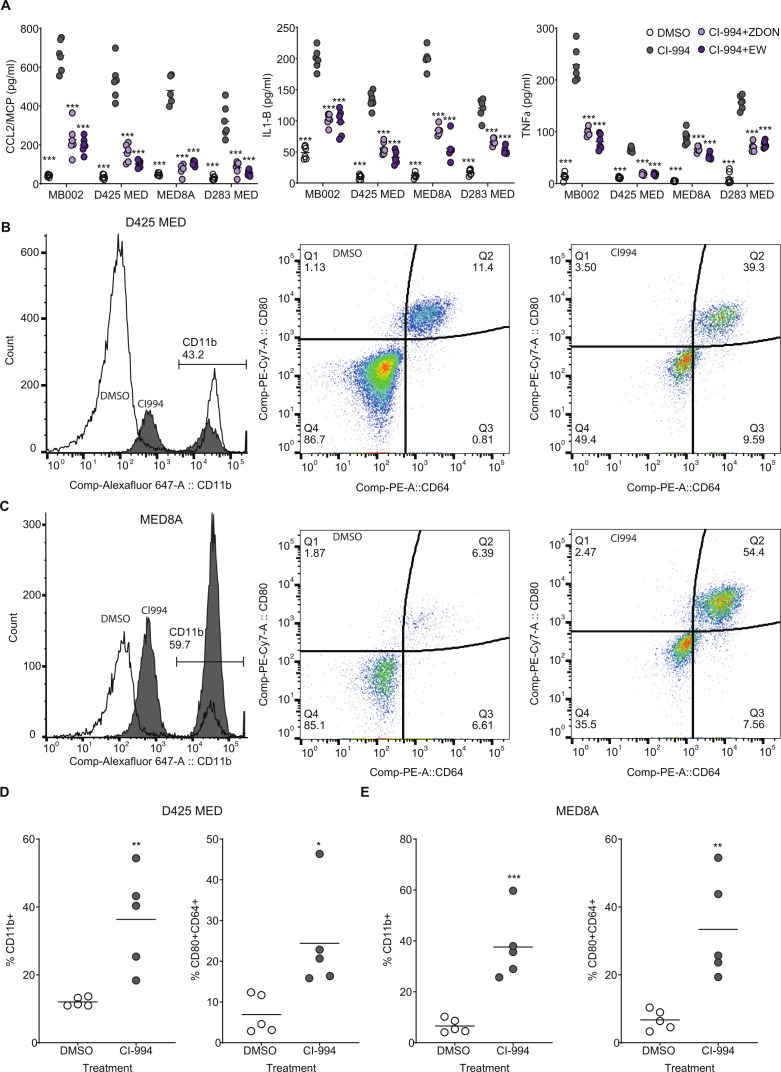
Figure 5.
CI-994 induces a TGM2-dependent pro-inflammatory cytokine response from tumor cells and an increase in infiltration of pro-inflammatory macrophages within tumors: (A) Essay for secretion of CCL1, interleukin-1B, and TNF-α was carried out by ELISA. Significant increase (***p<0.001: ordinary one-way analysis of variance) in the secretion of all three cytokines was observed in MB002, D425MED, MED8A, and D283MED cell lines on treatment with 5 µM CI-994. We also observed a significant drop in secretion of all three cytokines on inhibition of TGM2 using two different inhibitors, ZDON and ERW1041E. (B–C) Representative data from In vivo analysis of macrophage infiltration of macrophages in NSG mice with D425MED (B) or MED8A (C) cells xenografted into the cerebellum. Tumors were harvested and analyzed for total macrophage infiltration as identified being GFP– (tumors cells) and CD11b+. Increase in pro-inflammatory macrophages (CD45+CD11b+CD80+CD64+) is seen in CI-994 treated animals as compared with DMSO control. (D) Quantitative presentation of flow cytometry analysis from B and C. significant increase in CD11b+ macrophages (**p<0.01; n=5) and CD80+CD64+ (*p<0.05; n=5) was observed in D425MED cells whereas higher infiltration was observed in CD11b+ (***p<0.001; n=5) and CD80+CD64+ (**p<0.01; n=5 each). Each data point is an individual tumor-bearing mouse. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; TGM2, transglutaminase 2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.