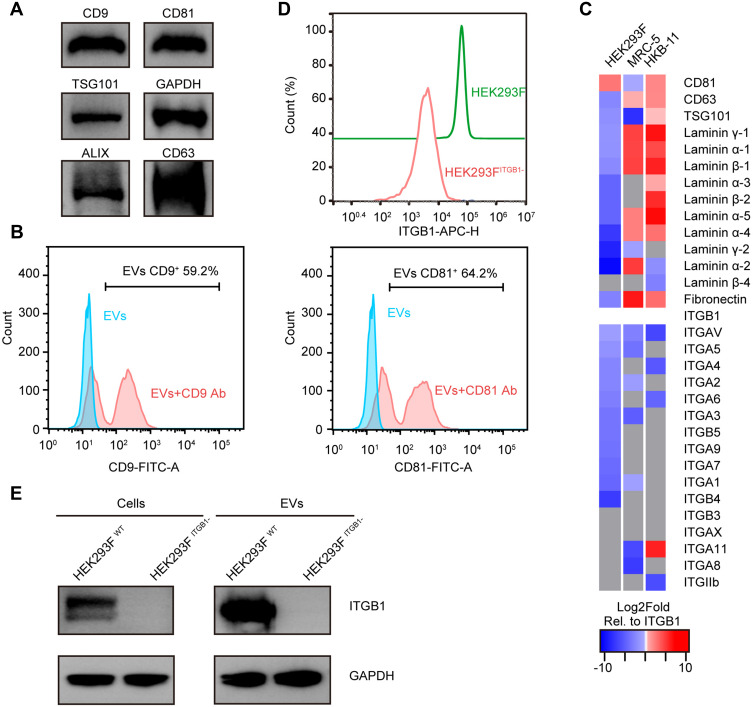
Figure 1.
Comparisons of surface markers and immunogenic protein levels in HEK293F and EVs derived from this cell line. (A) Western blot (WB) of HEK293F-derived EVs for Alix, CD9, CD63, CD81, and TSG101 protein levels. GAPDH served as the loading control. (B) Nanoflow cytometry (NanoFCM) of HEK293F-EVs labeled with anti-CD9, and anti-CD81 antibodies, respectively. (C) Log2Fold abundance of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), and standard EVs biomarkers such as CD81, CD63, and TSG101, normalized to the abundance of ITGB1 in respective EVs subtypes (proteins absent in the cellular proteome are marked as gray tiles, the Log2Fold abundance of ITGB1 in each cell line is 0 and colored white). (D) Flow cytometry analysis of WT and ITGB1− HEK293F cells stained with APC-conjugated anti-ITGB1 antibody confirmed that the ITGB1 expression was significantly diminished by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout (KO). (E) WB of cells (left) and EVs (right) from WT and ITGB1− HEK293F cells, respectively, further validated the absence of ITGB1 in both WT and ITGB1 KO HEK293F cells.