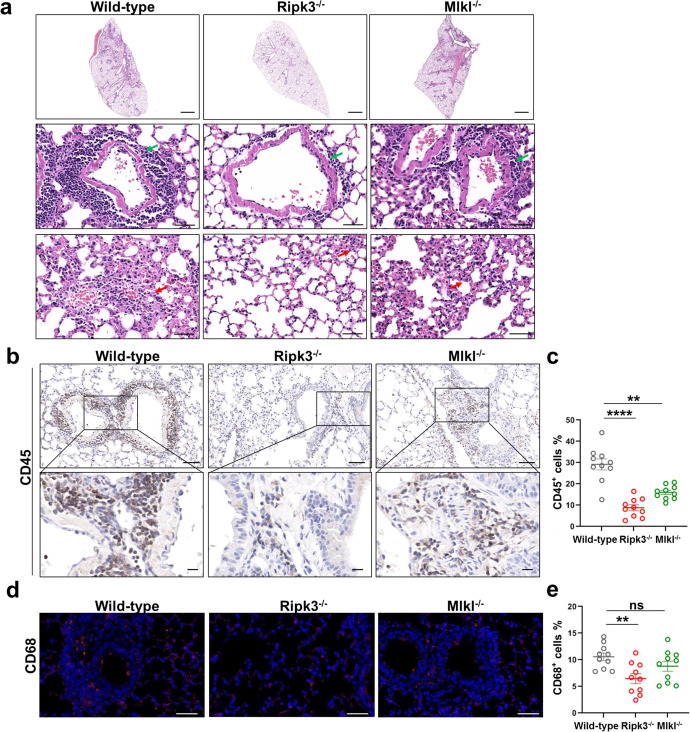
Fig. 6. RIPK3 contributes to SARS-CoV-2-induced lung damage and immune cell infiltration into the lung.
a–e Ad5-hACE2 (2.5 × 108 PFU) transduced Ripk3−/−, Mlkl−/− or wild-type C57BL/6 mice were infected with SARS-CoV-2 (1 × 105 TCID50). Lung samples were harvested at 2 dpi. a The histopathological changes were evaluated by H&E staining. Inflammatory cell infiltration (green arrow) and alveolar septa expansion (red arrow) were indicated. Scale bars, 1000 μm in the original image and 50 μm in the enlarged image. b–j Immunostaining of CD45 (b), CD68 (d), CD3 (f) and MPO (h) representing the infiltration of leukocytes, macrophages, T cells and neutrophils respectively. b, f Scale bars, 50 μm and 10 μm in the enlarged image. d, h Scale bars, 50 μm. c, e, g, i Quantitative analysis of positive cells performed with ImageJ for b, d, f, h, respectively. Data shown are means ± SEM. Statistical significance was analyzed by Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; **** P < 0.0001; ns, no significance. j Co-staining of CD8 (red) and CXCR3 (green) representing the recruitment of CD8+CXCR3+ T cells in the lung section of SARS-CoV-2-infected wild-type and Ripk3−/− mice. Scale bars, 10 μm.