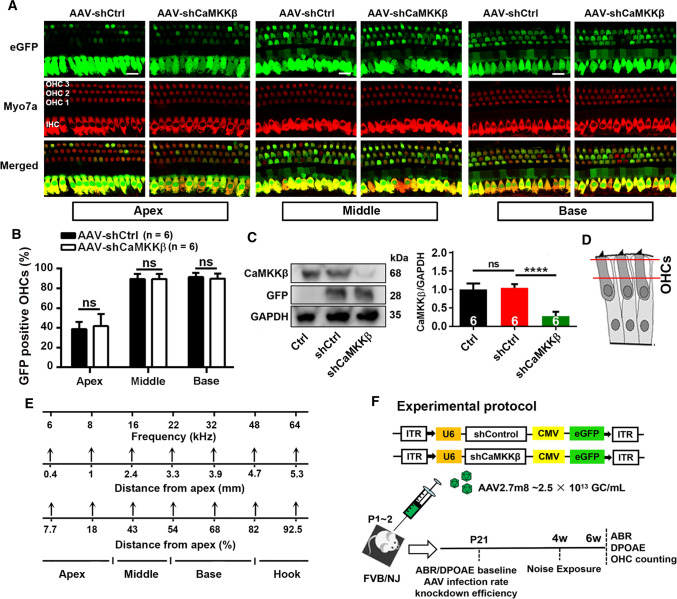
Fig. 1.
Application of shCaMKKβ via adeno-associated virus transduction significantly reduces CaMKKβ expression in the inner ear of FVB/NJ mice. A Representative images show AAV-infected sensory hair cell expression of eGFP (green) in the apical, middle, and basal turns co-localized by immunolabeling for myosin VIIa (Myo7a, red). Cochleae were harvested at p21 after microinjection of 2 µL of AAV-shControl (shCtrl) or AAV-shCaMKKβ stock solutions (2.5 × 1013 GC/mL) into the left ear of FVB/NJ mice at p1–2. eGFP: enhanced green fluorescent protein, Myo7a: myosin VIIa antibody used as a specific marker for sensory hair cells, shCtrl: scrambled shRNA, AAV-shCtrl: AAV2.7m8-U6-shControl-CMV-eGFP, and AAV-shCaMKKβ: AAV2.7m8-U6-shCaMKKβ-CMV-eGFP. Scale bar = 10 µm. B Counts of the eGFP-positive sensory hair cells show there was no difference in the infection rates between shCtrl and shCaMKKβ in OHCs and inner hair cells (IHCs) with an infection rate in IHCs of nearly 100% and 90% in OHCs in the middle and basal turns and 40% in OHCs in the apical turn. Data are presented as means + SD, n = 6 in each group, ns not statistically significant. C Representative images of immunoblots using inner ear homogenates revealed the bands of CaMKKβ, GFP, and GAPDH. GFP served as the transfection marker and GAPDH as the sample loading control. Quantification of the CaMKKβ band density shows significant reduction by 70% in shCaMKKβ via virus transduction compared with shCtrl mice. Data are presented as means + SD, n = 6 in each group, ****p < 0.0001. D The schematic diagram of OHCs indicates the plane from which confocal immunofluorescence images were captured, the cytosolic area between the two red lines. OHCs indicate outer hair cells. E A schematic diagram indicates mapping of frequencies along the entire cochlear spiral. F This diagram illustrates the AAV vector plasmid and the experimental timeline in FVB/NJ mice