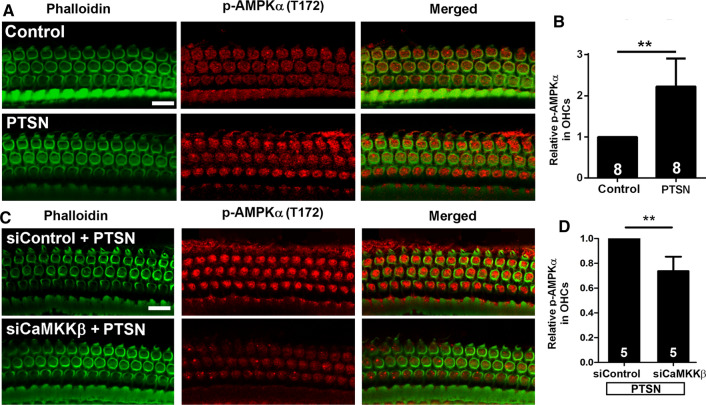
Fig. 10.
Silencing CaMKKβ decreases PTS-noise-increased p-AMPKα in OHCs of CBA/J mice. A Representative images show that PTSN exposure increases p-AMPKα (T172) in OHCs assessed 1–3 h after the exposure. B Semi-quantification of p-AMPKα (T172) in OHCs of the basal turn confirms a significant increase by exposure to PTSN. C Representative images show that the PTSN-induced increase in p-AMPKα (T172) immunolabeling (red) is reduced by siCaMKKβ compared to those of siControl mice examined 1–3 h after the exposure. D Semi-quantification of p-AMPKα (T172) in the basal turn confirms a significant decrease in siCaMKKβ-treated cochleae. All representative images are from the basal turn, corresponding to sensitivities to 30–32 kHz. Green: phalloidin-stained OHCs. Scale bar = 10 µm. Data for all bar graphs are presented as means + SD, and analyzed by one-sample t tests (B, D, and F). The number of animals in each group is indicated in the bar graph, **p < 0.01