Fig. 3.
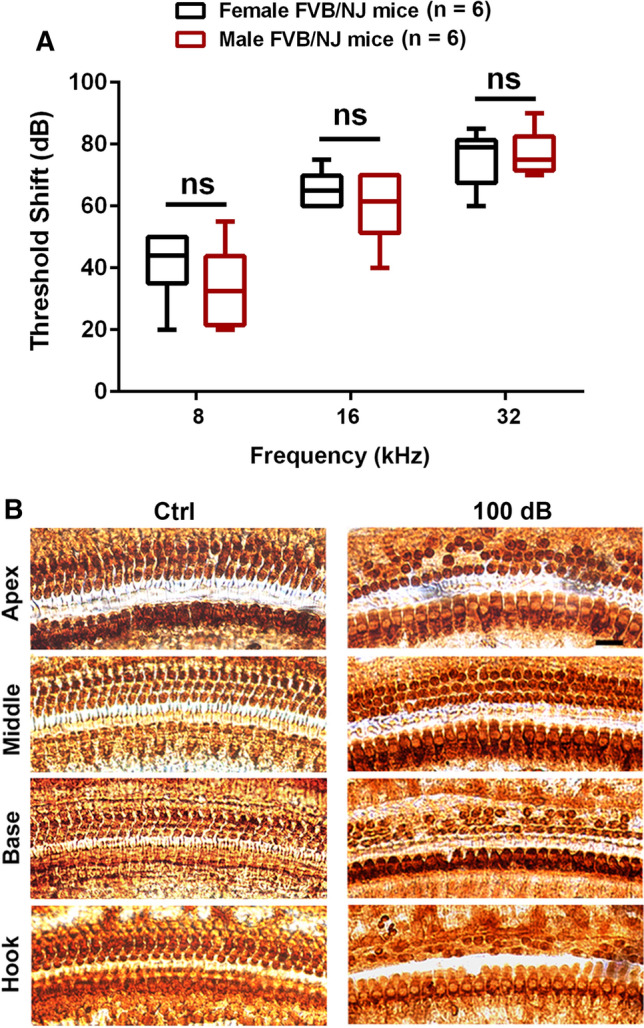
Noise-induced hearing loss is similar between male and female FVB/NJ mice exposed at the age of 4 weeks. A Auditory threshold shifts were calculated as baseline thresholds (before exposure) subtracted from thresholds 14 d post-exposure for each individual mouse. Noise exposure at 100 dB for 2 h induces hearing loss at all three measured frequencies (8, 16, and 32 kHz) that is more severe at higher frequencies than lower frequencies in both male and female mice. Data are presented as means with minimum-to-maximum ranges, ns indicates no statistical difference between males and females. B Representative microscope images were
taken from the apical, middle, basal, and hook turns of whole mount surface preparations immunolabeled with myosin VIIa and then stained with DAB to illustrate OHCs and IHCs. OHC 1, 2, 3, and IHC indicate three rows of outer hair cells and one row of inner hair cells. Counts of OHC loss are shown in Fig. 4A. These images are representative of six mice for each group. Scale bar = 10 µm
