Figure 1. Biochemical methods for identification and detection of SSG.
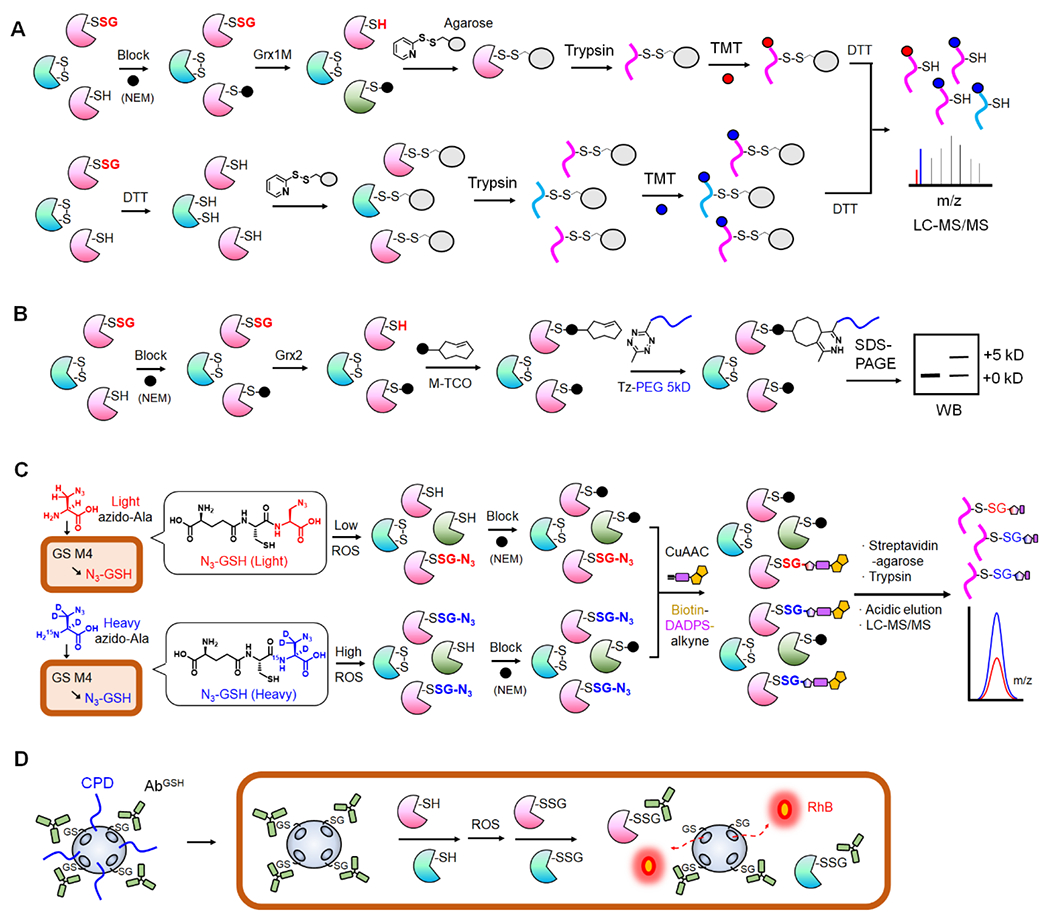
A. Grx-mediated detection of SSG or RAC-TMT. SSG is selectively reduced by Grx1 mutant (Grx1M) after blocking Cys with N-ethylmaleimide (NEM, black circle). Disulfide-based agarose captures reduced Cys in proteins (top). In parallel, all Cys-containing peptides from the same sample are captured on agarose after reducing with dithiothreitol (DTT, bottom). After trypsin digestion and TMT labeling, the bound peptides are eluted and combined for LC-MS/MS analysis to determine SSG levels. B. Grx-mediated SSG analysis with click chemistry. After selective reduction of SSG by Grx, the revealed Cys is reacted with maleimide-conjugated trans-cyclooctene (M-TCO). The subsequent reaction with 5-kD PEG-conjugated tetrazine (Tz-PEG) enables analysis of SSG levels via western blot. C. Glutathione synthetase mutant (GS M4)-based clickable glutathione. GS M4 uses light or heavy azido-Ala to synthesize isotopically labelled azido-GSH (N3-GSH) in cells. Isotopically labelled glutathionylated proteins (P-SSG) are combined, modified with biotin-DADPS-alkyne by click chemistry, captured on streptavidin-agarose, and digested by trypsin. The acidic cleavage of the DADPS linker enables elution of SSG-modified peptides for relative quantitation of SSG. D. Nanoparticle to image SSG in live cells. Mesoporous nanoparticle doped with black hole quenchers (qMSN) encapsulates and quenches rhodamine B (RhB). qMSN is modified with GSH on the surface, which binds to the GSH antibody (AbGSH) that blocks the release of RhB. The cell-penetrating disulfides (CPD) of qMSN enable its cell entry where SSG proteins (P-SSG) cause dissociation of AbGSH and releases of RhB, restoring fluorescence.
