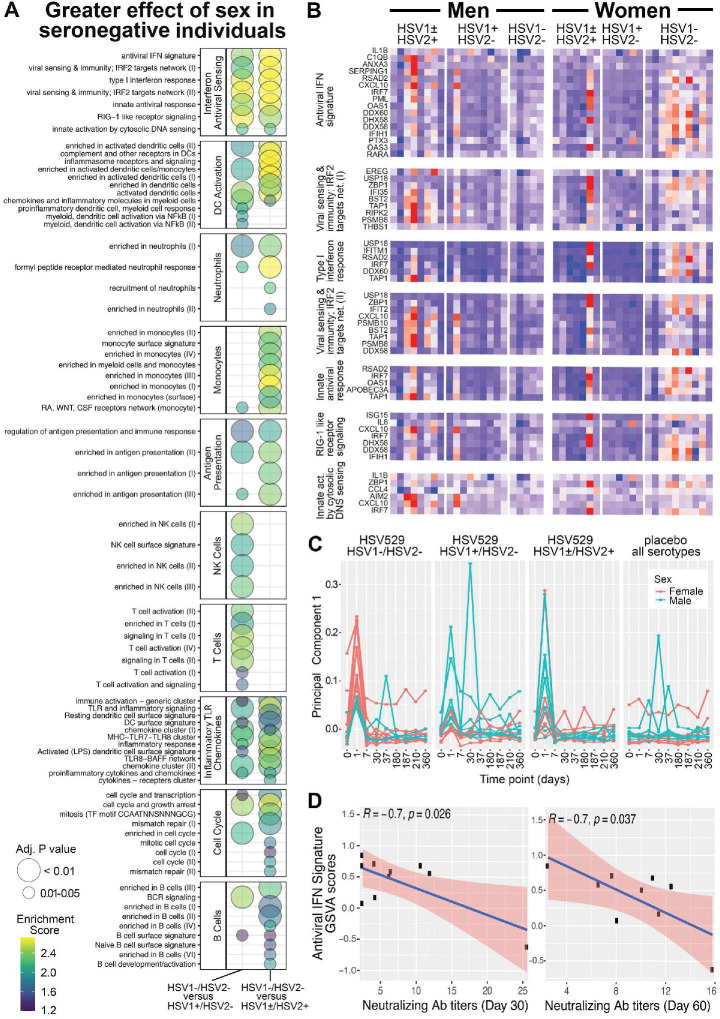
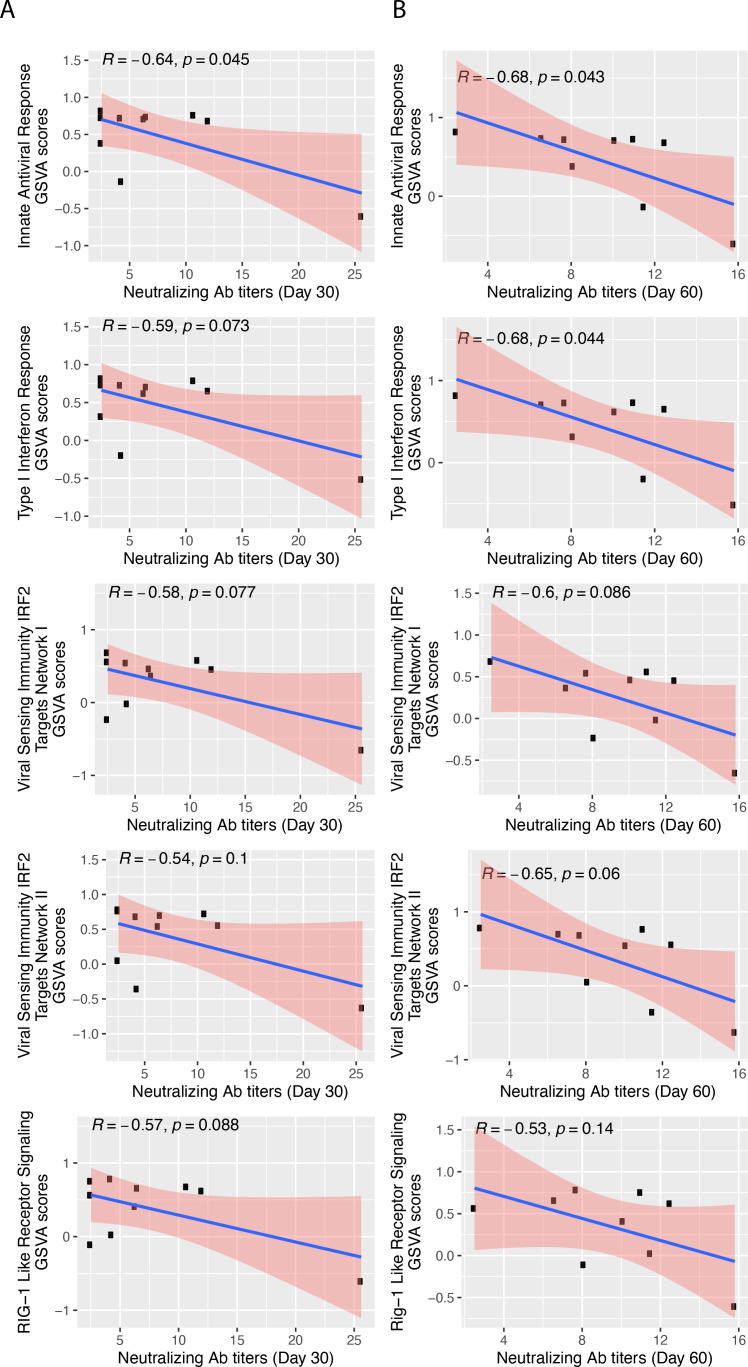
Figure 4. Gene expression responses to HSV529 that associate with sex differ significantly between subjects previously naive or exposed to herpes simplex virus (HSV), and the interferon (IFN) response associated with HSV naive women correlates inversely with HSV2 neutralizing antibody titers.
(A) Changes in expression of all genes between days 0 and 1 were compared between men and women separately for the three HSV serogroups of subjects based on prior exposure to HSV. For each gene those changes with sex were then used to compute a difference between the HSV naive group and either HSV exposed group (x-axis). These differences were used to rank genes for hypergeometric enrichment analysis of blood transcription modules (BTMs), and all pathways with significant positive enrichment in the HSV naive group are shown (FDR adjusted p < 0.05), with enrichment score and significance indicated by plotted color and size, respectively. (B) Comparison of sex differences between HSV naive and HSV1+/HSV2− subjects identified seven gene sets significantly enriched in the IFN antiviral sensing module. For these seven gene sets, responses of the 33 different leading-edge genes in rows, for all 45 vaccine recipients in columns are shown with the change in expression at day 1 compared to day 0 with z-scores normalized within each gene set, where red indicates above and blue indicates below mean values. (C) Principal component analysis was performed using expression of the 33 leading-edge genes from panel B, at all nine timepoints with RNA-seq data. The first principal component is plotted for all 60 subjects colored by sex and separated by HSV serostatus for vaccine recipients, or with all serogroups combined for placebo recipients. (D) For HSV naive women that were vaccinated, variation in day 1 IFN responses was quantified by gene set variation analysis (GSVA) of the antiviral IFN signature (y-axis), and correlated with HSV2 neutralizing antibody titers observed at day 30 or 60 (x-axis). Pearson coefficient and significance values are shown for the linear correlation in blue, with 95% confidence interval shaded red.