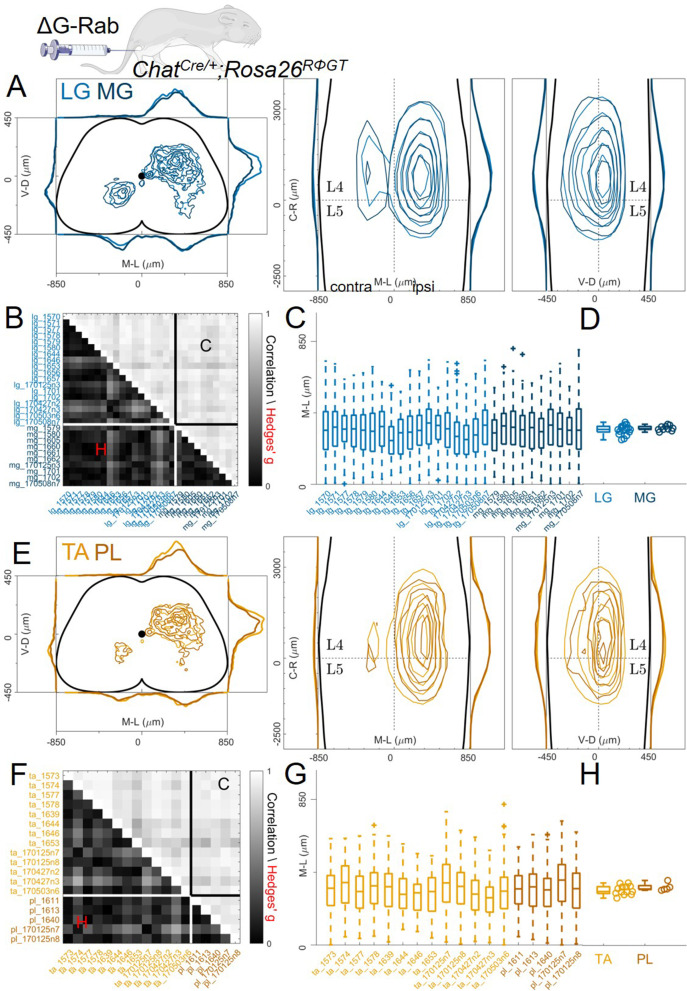
Figure 5. Pairs of flexor or extensor muscles show similar distributions of premotor interneurons.
(A) Comparison of pooled data from extensor muscles LG and MG injections. (B) Correlation and absolute value of Hedges’ G coefficients across all experiments. (C) Box and whisker plots of the mediolateral position of dorsal ipsilateral premotor interneurons for each experiment and distribution of median values (D). (E) Similar plot as A, showing the distribution of premotor interneurons following injections of the flexor muscles TA and PL. Correlations and absolute value of Hedges’ G coefficients across each experiment are shown in (F). (G and H) shows the mediolateral distribution and the position of the median for each experiment, respectively. For each section, the data are scaled to the reference points indicated in the methods in order to account for size differences along the segments.