Figure 7.
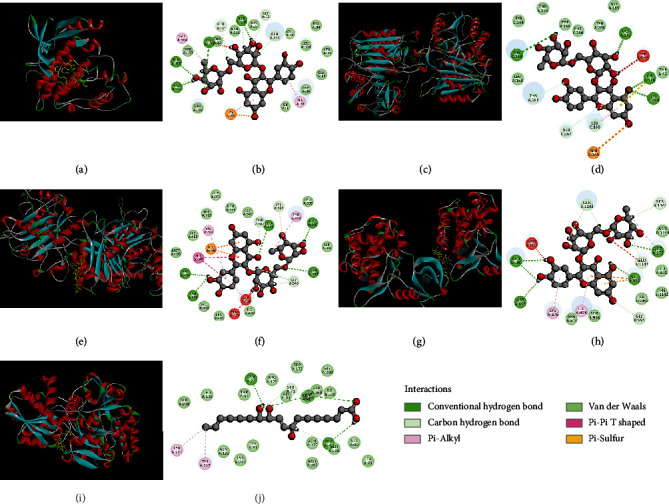
The represented results for the action mode of active compounds with 5 targets protein using molecular docking. (a, b) Action mode of rutin with target EGFR (PDB ID: 4RJ3): rutin has conventional hydrogen bonding interactions with ASP145, LYS129, THR165, and VAL163 of EGRF; carbon hydrogen bonding interactions with GLY13, GLN131, and GLU12; Pi-alkyl interactions with VAL164 and ILE10; Pi-Sulfur interaction with LYS88. (c, d) Action mode of rutin with CASP3 (PDB ID: 3DEK): rutin has conventional hydrogen bonding interactions with THR166, OSC163, CYS170, and LYS259 of CASP3; carbon hydrogen bonding interactions with THR166, LEU168, and GLU167; Pi-Sulfur interaction with ARG144. (e, f) Action mode of rutin with TNF (PDB ID: 2I47): rutin has conventional hydrogen bonding interactions with TYR436, VAL434, ASN389, GLU398, and LEU348 of TNF; carbon hydrogen bonding interactions with THR347, GLY346, and LYS392; Pi-Pi T shape interaction with HIS405; Pi-alkyl interactions with VAL402 and TYR390; Pi-Sulfur interaction with GLU406. (g, h) Action mode of rutin with STAT3 (PDB ID: 5E1E): rutin has conventional hydrogen bonding interactions with ASN900, ASP895, ASP992, and ARG879 of STAT3; carbon hydrogen bonding interactions with GLN1143, SER1141, GLU1147t, and GLY995; Pi-alkyl interactions with LYS876 and ILE878. (i, j) Action mode of tianshic acid with target ERBB2 (PDB ID: 3PPO): tianshic acid has conventional hydrogen bonding interactions with ASN72, GLY70, and GLN39 of ERBB2; Pi-alkyl interactions with TYR137 and TYR217.
