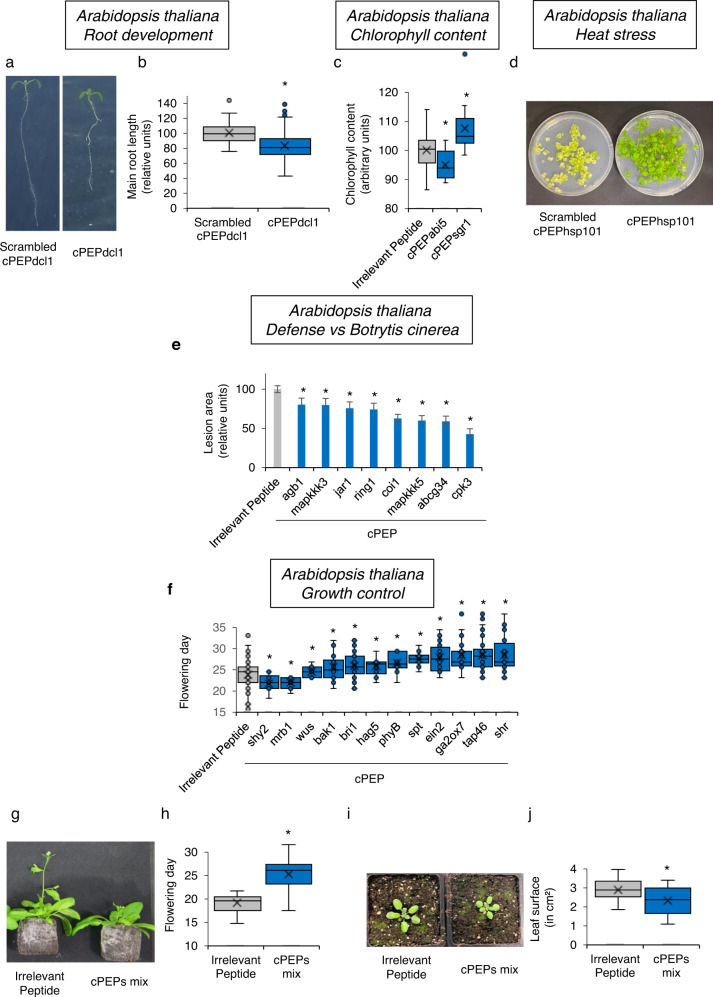
Fig. 3. cPEPs can modulate A. thaliana development and response to stresses.
a, b Primary root length of A. thaliana seedlings treated with Scrambled cPEPdcl1 or cPEPdcl1. c Relative chlorophyll content of A. thaliana plants treated with the indicated peptide. d Growth recovery of A. thaliana seedlings after a heat shock of 45 °C for 45 min and treated with the indicated peptide. e Relative lesion area of A. thaliana plants infected by B. cinerea and treated with the indicated peptide. f Measurement of the flowering day of A. thaliana plants treated with the indicated peptides. g, h Measurement of the flowering day of A. thaliana plants treated with an irrelevant peptide or a mix of cPEPs (targeting EIN2, BRI1, BAK1, and WUS). i, j Leaf surface of A. thaliana plants treated with an irrelevant peptide or a mix of cPEPs (targeting EIN2, BRI1, BAK1, and WUS). For box plots, the cross represents the mean, the line shows the median value, and the upper part and lower part of the box represent the first and third quartiles. The error bars represent the minimal and maximal value for box plots and the standard error of the mean (SEM) for others. Asterisks indicate a significant difference between the test condition and the control according to the Student t-test (b, c, e, f, h, j) (b n = 200; c, e, f, h, j n = 40; d n = 5; p < 0.05). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.